CD49d expression is an independent predictor of overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a prognostic parameter with therapeutic potential
- PMID: 18275431
- PMCID: PMC4477272
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06965.x
CD49d expression is an independent predictor of overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a prognostic parameter with therapeutic potential
Abstract
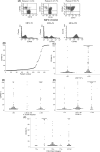
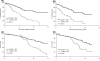
In vitro studies have demonstrated that surface expression of CD49d on chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) B cells facilitates leukaemic cell-stromal interactions by binding to fibronectin. This interaction reduces both spontaneous and drug-induced apoptosis. The present study measured CD49d expression by flow cytometry in a cohort of untreated CLL patients previously accrued to a prospective observational study and evaluated the relationship with overall survival (OS). Among the 158 CLL patients tested, the percentage of leukaemic B cells expressing CD49d ranged from 0 to 100%. When all risk factors were treated as continuous variables, CD49d expression showed moderate correlation with expression of ZAP-70 (r = 0.54; P < 0.0001) and CD38 (r = 0.58; P < 0.0001) but not %IGHV mutation. As a continuous variable, CD49d expression strongly correlated with OS (P < 0.0001). Recursive partitioning analysis suggested the 45% threshold of CD49d expression best predicted OS. Multivariate analysis, controlling for disease stage, ZAP-70, IGHV status and fluorescent in situ hybridization defects identified CD49d as an independent predictor of OS and was a better predictor of clinical outcome than ZAP-70, IGHV, or cytogenetics. This observational cohort study suggests that CLL B-cell expression of CD49d is an easily measurable and independent predictor of OS and CD49d expression in CLL. Importantly, anti-CD49d antibodies are already approved for treatment of other human diseases. Clinical testing of anti-CD49d therapy in CLL appears warranted.
Figures

Comment in
-
CD49d expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a prognostic parameter and a therapeutic target.Future Oncol. 2008 Jun;4(3):355-8. doi: 10.2217/14796694.4.3.355. Future Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18518761 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baldini L, Cro L, Calori R, Nobili L, Silvestris I, Maiolo AT. Differential expression of very late activation antigen-3 (VLA-3)/VLA-4 in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1992;79:2688–2693. - PubMed
-
- Behr SI, Korinth D, Schriever F. Differential adhesion pattern of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 1998;12:71–77. - PubMed
-
- Burger JA, Burger M, Kipps TJ. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express functional CXCR4 chemokine receptors that mediate spontaneous migration beneath bone marrow stromal cells. Blood. 1999;94:3658–3667. - PubMed
-
- Burger JA, Tsukada N, Burger M, Zvaifler NJ, Dell'Aquila M, Kipps TJ. Blood-derived nurse-like cells protect chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from spontaneous apoptosis through stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood. 2000;96:2655–2663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

