Expression of recombinant Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, R. annulatus and R. decoloratus Bm86 orthologs as secreted proteins in Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 18275601
- PMCID: PMC2262073
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-8-14
Expression of recombinant Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, R. annulatus and R. decoloratus Bm86 orthologs as secreted proteins in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
Background: Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) spp. ticks economically impact on cattle production in Africa and other tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Tick vaccines constitute a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to tick control. The R. microplus Bm86 protective antigen has been produced by recombinant DNA technology and shown to protect cattle against tick infestations.
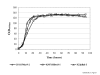
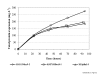
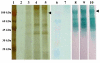
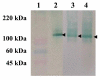
Results: In this study, the genes for Bm86 (R. microplus), Ba86 (R. annulatus) and Bd86 (R. decoloratus) were cloned and characterized from African or Asian tick strains and the recombinant proteins were secreted and purified from P. pastoris. The secretion of recombinant Bm86 ortholog proteins in P. pastoris allowed for a simple purification process rendering a final product with high recovery (35-42%) and purity (80-85%) and likely to result in a more reproducible conformation closely resembling the native protein. Rabbit immunization experiments with recombinant proteins showed immune cross-reactivity between Bm86 ortholog proteins.
Conclusion: These experiments support the development and testing of vaccines containing recombinant Bm86, Ba86 and Bd86 secreted in P. pastoris for the control of tick infestations in Africa.
Figures
References
-
- Estrada-Peña A, Bouattour A, Camicas JL, Guglielmone A, Horak I, Jongejan F, Latif A, Pegram R, Walker AR. The known distribution and ecological preferences of the tick subgenus Boophilus (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa and Latin America. Exp Appl Acarol. 2006;38:219–235. doi: 10.1007/s10493-006-0003-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Olwoch JM, Van Jaarsveld AS, Scholtz CH, Horak IG. Climate change and the genus Rhipicephalus (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 2007;74:45–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

