CD163, a marker of perivascular macrophages, is up-regulated by microglia in simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis after haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex stimulation and is suggestive of breakdown of the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 18276779
- PMCID: PMC2258269
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070848
CD163, a marker of perivascular macrophages, is up-regulated by microglia in simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis after haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex stimulation and is suggestive of breakdown of the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
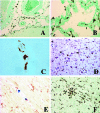
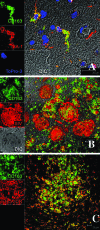
Macrophages and microglia are the major cell types infected by human immunodeficiency virus and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) in the central nervous system. Microglia are likely infected in vivo, but evidence of widespread productive infection (ie, presence of viral RNA and protein) is lacking. This conclusion is controversial because, unlike lymphocytes, macrophages and microglia cannot be discreetly immunophenotyped. Of particular interest in the search for additional monocyte/macrophage-lineage cell markers is CD163; this receptor for haptoglobin-hemoglobin (Hp-Hb) complex, which forms in plasma following erythrolysis, is expressed exclusively on cells of monocyte/macrophage lineage. We examined CD163 expression in vitro and in vivo by multiple techniques and at varying times after SIV infection in macaques with or without encephalitis. In normal and acutely SIV-infected animals, and in SIV-infected animals without encephalitis, CD163 expression was detected in cells of monocyte/macrophage lineage, including perivascular macrophages, but not in parenchymal microglia. However, in chronically infected animals with encephalitis, CD163 expression was detected in activated microglia surrounding SIV encephalitis lesions in the presence of Hp-Hb complex, suggesting leakage of the blood-brain barrier. CD163 expression was also induced on microglia in vitro after stimulation with Hp-Hb complex. We conclude that CD163 is a selective marker of perivascular macrophages in normal macaques and during the early phases of SIV infection; however, later in infection in animals with encephalitis, CD163 is also expressed by microglia, which are probably activated as a result of vascular compromise.
Figures



References
-
- Albright AV, Shieh JT, O'Connor MJ, Gonzalez-Scarano F. Characterization of cultured microglia that can be infected by HIV-1. J Neurovirol. 2000;6(Suppl 1):S53–S60. - PubMed
-
- Albright AV, Gonzalez-Scarano F. Microarray analysis of activated mixed glial (microglia) and monocyte-derived macrophage gene expression. J Neuroimmunol. 2004;157:27–38. - PubMed
-
- Clements JE, Babas T, Mankowski JL, Suryanarayana K, Piatak M, Jr, Tarwater PM, Lifson JD, Zink MC. The central nervous system as a reservoir for simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV): steady-state levels of SIV DNA in brain from acute through asymptomatic infection. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:905–913. - PubMed
-
- Zink MC, Spelman JP, Robinson RB, Clements JE. SIV infection of macaques—modeling the progression to AIDS dementia. J Neurovirol. 1998;4:249–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

