Persistent human immunodeficiency virus-1 antigenaemia affects the expression of interleukin-7Ralpha on central and effector memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets
- PMID: 18279439
- PMCID: PMC2384057
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03610.x
Persistent human immunodeficiency virus-1 antigenaemia affects the expression of interleukin-7Ralpha on central and effector memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets
Abstract
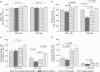
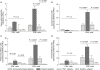
Interleukin (IL)-7 and its receptor (IL-7Ralpha) play important roles in regulating lymphopoiesis. Previous studies have reported that human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) viraemia affects the expression of IL-7Ralpha, but its effects on CD4+ and CD8+ T cell memory subsets have not been studied. Using eight-colour flow cytometry, we compared the immunophenotypic patterns of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets expressing IL-7Ralpha and activation markers, as well as circulating IL-7 levels, in three well-defined groups of HIV-1-infected subjects: successfully treated, viraemic and long-term non-progressor (LTNP). Compared with successfully treated and LTNP subjects, viraemic patients had reduced expression of IL-7Ralpha on both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, particularly on central and effector memory T cell compartments, and substantially elevated expression of activation markers on CD8+ T cell subsets. Circulating IL-7 levels were correlated negatively with the number of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets expressing IL-7Ralpha; these associations were stronger with CD4+ T cell subsets and mainly with central and effector memory cells. The expression of activation markers on CD4+ and CD8+ cell T subsets was not related to circulating IL-7 levels. A strong negative correlation was observed between central memory CD4+ or CD8+ T cells expressing IL-7Ralpha and those expressing activation markers, independently of IL-7 levels. Collectively, these results provide further insight on the role of unsuppressed viral load in disrupting the IL-7/IL-7Ralpha system and contributing to HIV-1 disease progression.
Figures


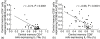
References
-
- McCune JM. The dynamics of CD4+ T-cell depletion in HIV disease. Nature. 2001;410:974–9. - PubMed
-
- Hazenberg MD, Hamann D, Schuitemaker H, Miedema F. T cell depletion in HIV-1 infection: how CD4+ T cells go out of stock. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:285–9. - PubMed
-
- Boulassel MR, Smith GH, Gilmore N, et al. Interleukin-7 levels may predict virological response in advanced HIV-1-infected patients receiving lopinavir/ritonavir-based therapy. HIV Med. 2003;4:315–20. - PubMed
-
- Boulassel MR, Smith GH, Edwardes MD, et al. Influence of RANTES, SDF-1 and TGF-beta levels on the value of interleukin-7 as a predictor of virological response in HIV-1-infected patients receiving double boosted protease inhibitor-based therapy. HIV Med. 2005;6:268–77. - PubMed
-
- Sasson SC, Zaunders JJ, Zanetti G, et al. Increased plasma interleukin-7 level correlates with decreased CD127 and increased CD132 extracellular expression on T cell subsets in patients with HIV-1 infection. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:505–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

