Regulation of the development of tectal neurons and their projections by transcription factors Brn3a and Pax7
- PMID: 18280463
- PMCID: PMC2396191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.12.040
Regulation of the development of tectal neurons and their projections by transcription factors Brn3a and Pax7
Abstract
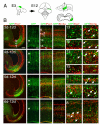
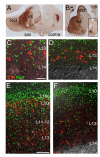
The rostral part of the dorsal midbrain, known as the superior colliculus in mammals or the optic tectum in birds, receives a substantial retinal input and plays a diverse and important role in sensorimotor integration. However, little is known about the development of specific subtypes of neurons in the tectum, particularly those which contribute tectofugal projections to the thalamus, isthmic region, and hindbrain. Here we show that two homeodomain transcription factors, Brn3a and Pax7, are expressed in mutually exclusive patterns in the developing and mature avian midbrain. Neurons expressing these factors are generated at characteristic developmental times, and have specific laminar fates within the tectum. In mice expressing betagalactosidase targeted to the Pou4f1 (Brn3a) locus, Brn3a-expressing neurons contribute to the ipsilateral but not the contralateral tectofugal projections to the hindbrain. Using misexpression of Brn3a and Pax7 by electroporation in the chick tectum, combined with GFP reporters, we show that Brn3a determines the laminar fate of subsets of tectal neurons. Furthermore, Brn3a regulates the development of neurons contributing to specific ascending and descending tectofugal pathways, while Pax7 globally represses the development of tectofugal projections to nearly all brain structures.
Figures






References
-
- Agarwala S, Sanders TA, Ragsdale CW. Sonic hedgehog control of size and shape in midbrain pattern formation. Science. 2001;291:2147–50. - PubMed
-
- Bayly RD, Ngo M, Aglyamova GV, Agarwala S. Regulation of ventral midbrain patterning by Hedgehog signaling. Development. 2007;134:2115–2124. - PubMed
-
- Benowitz LI, Karten HJ. Organization of the tectofugal visual pathway in the pigeon: a retrograde transport study. J Comp Neurol. 1976;167:503–20. - PubMed
-
- Blaess S, Corrales JD, Joyner AL. Sonic hedgehog regulates Gli activator and repressor functions with spatial and temporal precision in the mid/hindbrain region. Development. 2006;133:1799–809. - PubMed
-
- Crossley PH, Martinez S, Martin GR. Midbrain development induced by FGF8 in the chick embryo. Nature. 1996;380:66–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

