Ecstasy (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) limits murine gammaherpesvirus-68 induced monokine expression
- PMID: 18280699
- PMCID: PMC4275657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2008.01.002
Ecstasy (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) limits murine gammaherpesvirus-68 induced monokine expression
Abstract
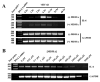
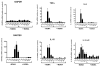
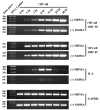
While Ecstasy (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, MDMA) has been shown to modulate immune responses, no studies have addressed drug-induced alterations to viral infection. In this study, bone marrow-derived macrophages were exposed to MDMA, then infected with murine gammaherpesvirus-68, and the expression of monokines assessed. MDMA-induced reductions in virus-stimulated monokine mRNA expression were observed in a dose-dependent manner. In particular, IL-6 mRNA expression and secretion was significantly decreased in gammaherpesvirus-infected macrophages exposed to MDMA. Concentrations of MDMA capable of reducing monokine production did not induce significant cell death and allowed normal viral gene expression. These studies represent the first to demonstrate the ability of this drug of abuse to alter a viral-induced macrophage response.
Figures



References
-
- Battaglia G, Brooks BP, Kulsakdinun C, De Souza EB. Pharmacologic profile of MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) at various brain recognition sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988;149:159–163. - PubMed
-
- Bowman CC, Bost KL. Cyclooxygenase-2-mediated prostaglandin E2 production in mesenteric lymph nodes and in cultured macrophages and dendritic cells after infection with Salmonella. J Immunol. 2004;172:2469–2475. - PubMed
-
- Boyle NT, Connor TJ. MDMA (“Ecstasy”) suppresses the innate IFN-gamma response in vivo: A critical role for the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;572:228–238. - PubMed
-
- Capela JP, Fernandes E, Remiao F, Bastos ML, Meisel A, Carvalho F. Ecstasy induces apoptosis via 5-HT(2A)-receptor stimulation in cortical neurons. Neurotoxicology. 2007;28:868–875. - PubMed
-
- Capela JP, Ruscher K, Lautenschlager M, Freyer D, Dirnagl U, Gaio AR, Bastos ML, Meisel A, Carvalho F. Ecstasy-induced cell death in cortical neuronal cultures is serotonin 2A-receptor-dependent and potentiated under hyperthermia. Neuroscience. 2006;139:1069–1081. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

