Impact of CYP2B6 983T>C polymorphism on non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor plasma concentrations in HIV-infected patients
- PMID: 18281305
- PMCID: PMC3596857
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkn029
Impact of CYP2B6 983T>C polymorphism on non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor plasma concentrations in HIV-infected patients
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate the frequency of CYP2B6 polymorphisms (according to ethnicity) and the influence of heterozygosity and homozygosity on plasma concentrations of efavirenz and nevirapine.
Methods: Following written informed consent, 225 Caucasians and 146 Blacks were recruited from the German Competence Network for HIV/AIDS. Plasma concentrations of efavirenz and nevirapine were assessed by HPLC, and genotyping for 516G>T, 983T>C and 1459T>C polymorphisms in CYP2B6 was conducted by real-time PCR-based allelic discrimination.
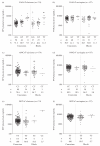
Results: The minor allele frequency for 516G>T, 983T>C and 1459T>C was 0.29, 0 and 0.08 in Caucasians and 0.34, 0.07 and 0.02 in Blacks, respectively. Two Black patients with the 983C allele receiving efavirenz were identified and both were withdrawn from therapy within 1 week of sampling due to toxicity. In multivariate analyses, efavirenz and nevirapine plasma concentrations were significantly associated with 983T>C (P < 0.0001 and P = 0.02, respectively), 516G>T (P < 0.0001 and P = 0.002, respectively) and time of drug analysis post-dose (P < 0.0001 for both). Body mass index was independently related to efavirenz (P = 0.04) but not nevirapine concentrations, and age was related to nevirapine (P = 0.05) but not efavirenz concentrations. Consistent with other studies, 1459C>T was not associated with plasma concentrations of either drug (P > 0.05 for both drugs).
Conclusions: This is the first report that the 983T>C genotype (part of the CYP2B6*18 haplotype) impacts on nevirapine plasma concentrations and the first study to assess the impact of 983C homozygosity on efavirenz concentrations. These data have implications for administration of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors to Black patients.
Figures
References
-
- Owen A, Pirmohamed M, Khoo SH, et al. Pharmacogenetics of HIV therapy. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2006;16:693–703. - PubMed
-
- Lang T, Klein K, Fischer J, et al. Extensive genetic polymorphism in the human CYP2B6 gene with impact on expression and function in human liver. Pharmacogenetics. 2001;11:399–415. - PubMed
-
- Haas DW, Bartlett JA, Andersen JW, et al. Pharmacogenetics of nevirapine-associated hepatotoxicity: an Adult AIDS Clinical Trials Group collaboration. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:783–6. - PubMed
-
- Haas DW, Ribaudo HJ, Kim RB, et al. Pharmacogenetics of efavirenz and central nervous system side effects: an Adult AIDS Clinical Trials Group study. AIDS. 2004;18:2391–400. - PubMed
-
- Ribaudo HJ, Haas DW, Tierney C, et al. Pharmacogenetics of plasma efavirenz exposure after treatment discontinuation: an Adult AIDS Clinical Trials Group Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:401–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

