Vascular dermatan sulfate regulates the antithrombotic activity of heparin cofactor II
- PMID: 18281504
- PMCID: PMC2288722
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-12-127928
Vascular dermatan sulfate regulates the antithrombotic activity of heparin cofactor II
Abstract
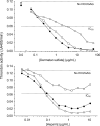
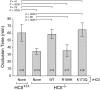
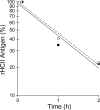
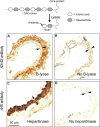
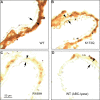
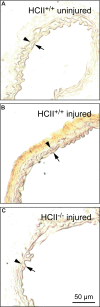
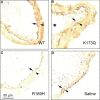
Heparin cofactor II (HCII)-deficient mice form occlusive thrombi more rapidly than do wild-type mice following injury to the carotid arterial endothelium. Dermatan sulfate (DS) and heparan sulfate (HS) increase the rate of inhibition of thrombin by HCII in vitro, but it is unknown whether vascular glycosaminoglycans play a role in the antithrombotic effect of HCII in vivo. In this study, we found that intravenous injection of either wild-type recombinant HCII or a variant with low affinity for HS (K173H) corrected the abnormally short thrombosis time of HCII-deficient mice, while a variant with low affinity for DS (R189H) had no effect. When HCII was incubated with frozen sections of the mouse carotid artery, it bound specifically to DS in the adventitia. HCII was undetectable in the wall of the uninjured carotid artery, but it became concentrated in the adventitia following endothelial injury. These results support the hypothesis that HCII interacts with DS in the vessel wall after disruption of the endothelium and that this interaction regulates thrombus formation in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Mann KG. Thrombin formation. Chest. 2003;124:4S–10S. - PubMed
-
- Coughlin SR. Protease-activated receptors in hemostasis, thrombosis and vascular biology. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:1800–1814. - PubMed
-
- Bock S. Antithrombin III and heparin cofactor II. In: Colman R, Marder V, Clowes A, George J, Goldhaber S, editors. Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. pp. 235–248.
-
- Tollefsen D, Zhang L. Heparin and vascular proteoglycans. In: Colman R, Marder V, Clowes A, George J, Goldhaber S, editors. Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. pp. 271–283.
-
- Tollefsen DM. Antithrombin deficiency. In: Scriver C, Beaudet A, Sly W, et al., editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 4455–4471.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

