LARP7 is a stable component of the 7SK snRNP while P-TEFb, HEXIM1 and hnRNP A1 are reversibly associated
- PMID: 18281698
- PMCID: PMC2367717
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn061
LARP7 is a stable component of the 7SK snRNP while P-TEFb, HEXIM1 and hnRNP A1 are reversibly associated
Abstract
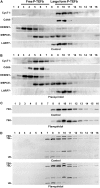
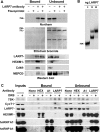
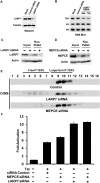
Regulation of the elongation phase of RNA polymerase II transcription by P-TEFb is a critical control point for gene expression. The activity of P-TEFb is regulated, in part, by reversible association with one of two HEXIMs and the 7SK snRNP. A recent proteomics survey revealed that P-TEFb and the HEXIMs are tightly connected to two previously-uncharacterized proteins, the methyphosphate capping enzyme, MEPCE, and a La-related protein, LARP7. Glycerol gradient sedimentation analysis of lysates from cells treated with P-TEFb inhibitors, suggested that the 7SK snRNP reorganized such that LARP7 and 7SK remained associated after P-TEFb and HEXIM1 were released. Immunodepletion of LARP7 also depleted most of the 7SK regardless of the presence of P-TEFb, HEXIM or hnRNP A1 in the complex. Small interfering RNA knockdown of LARP7 in human cells decreased the steady-state level of 7SK, led to an initial increase in free P-TEFb and increased Tat transactivation of the HIV-1 LTR. Knockdown of LARP7 or 7SK ultimately caused a decrease in total P-TEFb protein levels. Our studies have identified LARP7 as a 7SK-binding protein and suggest that free P-TEFb levels are determined by a balance between release from the large form and reduction of total P-TEFb.
Figures


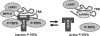
Similar articles
-
RNA elements directing in vivo assembly of the 7SK/MePCE/Larp7 transcriptional regulatory snRNP.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr;41(8):4686-98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt159. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23471002 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of release of P-TEFb and HEXIM1 from the 7SK snRNP by viral and cellular activators includes a conformational change in 7SK.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 23;5(8):e12335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012335. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808803 Free PMC article.
-
Release of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) from 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) activates hexamethylene bisacetamide-inducible protein (HEXIM1) transcription.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 4;289(14):9918-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.539015. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24515107 Free PMC article.
-
7SK RNA, a non-coding RNA regulating P-TEFb, a general transcription factor.RNA Biol. 2009 Apr-Jun;6(2):122-8. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.2.8115. Epub 2009 Apr 6. RNA Biol. 2009. PMID: 19246988 Review.
-
Cracking the control of RNA polymerase II elongation by 7SK snRNP and P-TEFb.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 19;44(16):7527-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw585. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27369380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LARP4B is an AU-rich sequence associated factor that promotes mRNA accumulation and translation.RNA. 2015 Jul;21(7):1294-305. doi: 10.1261/rna.051441.115. Epub 2015 May 22. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26001795 Free PMC article.
-
Gliotoxin, identified from a screen of fungal metabolites, disrupts 7SK snRNP, releases P-TEFb, and reverses HIV-1 latency.Sci Adv. 2020 Aug 12;6(33):eaba6617. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba6617. eCollection 2020 Aug. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32851167 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interplay between PPM1G and the transcription elongation machinery.RNA Dis. 2016;3(1):e1215. Epub 2016 Mar 14. RNA Dis. 2016. PMID: 27088130 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine prevents transcription inhibition and P-TEFb/7SK dissociation following UV-induced DNA damage.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 21;5(6):e11245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011245. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20574533 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the Ankyrin H Core Effector of Legionella with the Host LARP7 Component of the 7SK snRNP Complex.mBio. 2019 Aug 27;10(4):e01942-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01942-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31455655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peng J, Marshall NF, Price DH. Identification of a cyclin subunit required for the function of Drosophila P-TEFb. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:13855–13860. - PubMed
-
- Marshall NF, Peng J, Xie Z, Price DH. Control of RNA polymerase II elongation potential by a novel carboxyl-terminal domain kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:27176–27183. - PubMed
-
- Marshall NF, Price DH. Purification of P-TEFb, a transcription factor required for the transition into productive elongation. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:12335–12338. - PubMed
-
- Peterlin BM, Price DH. Controlling the elongation phase of transcription with P-TEFb. Mol. Cell. 2006;23:297–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

