Biologic treatments for systemic rheumatic diseases
- PMID: 18282173
- PMCID: PMC2766248
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2008.01440.x
Biologic treatments for systemic rheumatic diseases
Abstract
Many rheumatologic disorders, most notably Sjögren's syndrome, are associated with dental complications and in some cases oral diseases may trigger or drive connective tissue disease. During the past three decades the treatment in rheumatology was revolutionized by the introduction of disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Advances in our understanding of the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases have led to the discovery of critical mechanisms of inflammation and autoimmunity and the invention of new target-specific biologic agents. In this review, we will summarize the current state of biologic therapies in rheumatology and discuss the implications of these on oral health and disease.
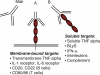
Figures
References
-
- Anolik JH, Barnard J, Cappione A, et al. Rituximab improves peripheral B cell abnormalities in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3580–3590. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson JC, Fox PC. Sjogren's syndrome: oral and dental considerations. J Am Dent Assoc. 1993;124:74–76. 78–82, 84–86. - PubMed
-
- Azuma M, Aota K, Tamatani T, et al. Suppression of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase 9 production in human salivary gland acinar cells by cepharanthine occurs via down-regulation of nuclear factor kappaB: a possible therapeutic agent for preventing the destruction of the acinar structure in the salivary glands of Sjogren's syndrome patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1585–1594. - PubMed
-
- Banner DW, D'Arcy A, Janes W, et al. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNF beta complex: implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell. 1993;73:431–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

