The yeast p24 complex is required for the formation of COPI retrograde transport vesicles from the Golgi apparatus
- PMID: 18283113
- PMCID: PMC2265561
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200710025
The yeast p24 complex is required for the formation of COPI retrograde transport vesicles from the Golgi apparatus
Abstract
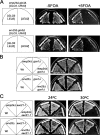
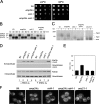
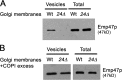
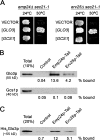
The p24 family members are transmembrane proteins assembled into heteromeric complexes that continuously cycle between the ER and the Golgi apparatus. These cargo proteins were assumed to play a structural role in COPI budding because of their major presence in mammalian COPI vesicles. However, this putative function has not been proved conclusively so far. Furthermore, deletion of all eight yeast p24 family members does not produce severe transport phenotypes, suggesting that the p24 complex is not essential for COPI function. In this paper we provide direct evidence that the yeast p24 complex plays an active role in retrograde transport from Golgi to ER by facilitating the formation of COPI-coated vesicles. Therefore, our results demonstrate that p24 proteins are important for vesicle formation instead of simply being a passive traveler, supporting the model in which cargo together with a small GTPase of the ARF superfamily and coat subunits act as primer for vesicle formation.
Figures
References
-
- Belden, W.J., and C. Barlowe. 2001. b. Distinct roles for the cytoplasmic tail sequences of Emp24p and Erv25p in transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. J. Biol. Chem. 276:43040–43048. - PubMed
-
- Bremser, M., W. Nickel, M. Schweikert, M. Ravazzola, M. Amherdt, C.A. Hughes, T.H. Sollner, J.E. Rothman, and F.T. Wieland. 1999. Coupling of coat assembly and vesicle budding to packaging of putative cargo receptors. Cell. 96:495–506. - PubMed
-
- Cox, J.S., and P. Walter. 1996. A novel mechanism for regulating activity of a transcription factor that controls the unfolded protein response. Cell. 87:391–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

