Regulation of apoptosis-inducing factor-mediated, cisplatin-induced apoptosis by Akt
- PMID: 18283299
- PMCID: PMC2259169
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604223
Regulation of apoptosis-inducing factor-mediated, cisplatin-induced apoptosis by Akt
Abstract
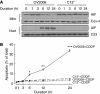
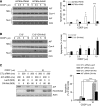
Cisplatin is a first-line chemotherapeutic for ovarian cancer, although chemoresistance limits treatment success. Apoptosis, an important determinant of cisplatin sensitivity, occurs via caspase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Activation of the protein kinase Akt, commonly observed in ovarian tumours, confers resistance to ovarian cancer cells via inhibition of caspase-dependent apoptosis. However, the effect of Akt on cisplatin-induced, caspase-independent apoptosis remains unclear. We show that in chemosensitive ovarian cancer cells, cisplatin induces the mitochondrial release and nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), a mediator of caspase-independent apoptosis, and AIF-dependent apoptosis. Cisplatin failed to induce these effects in the chemoresistant variant cells. Overexpression of AIF sensitised resistant cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Finally, activation of Akt attenuated the cisplatin-induced mitochondrial release and nuclear accumulation of AIF and apoptosis in chemosensitive cells, whereas inhibition of Akt activity facilitated these effects and sensitised chemoresistant cells to AIF-dependent, cisplatin-induced apoptosis. These results suggest that cisplatin-induced apoptosis proceeds, in part, via a caspase-independent mechanism involving AIF, and that Akt activation confers resistance to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by blocking this pathway. These results provide insights into the molecular mechanism of chemoresistance, and suggest that inhibition of Akt activity may represent a novel therapeutic approach to the treatment of cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Abedini MR, Qiu Q, Yan X, Tsang BK (2004) Possible role of FLICE-like inhibitory protein (FLIP) in chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Oncogene 23: 6997–7004 - PubMed
-
- Alfano D, Iaccarino I, Stoppelli MP (2006) Urokinase signaling through its receptor protects against anoikis by increasing BCL-xL expression levels. J Biol Chem 281: 17758–17767 - PubMed
-
- Asselin E, Mills GB, Tsang BK (2001) XIAP regulates Akt activity and caspase-3-dependent cleavage during cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human ovarian epithelial cancer cells. Cancer Res 61: 1862–1868 - PubMed
-
- Barton C, Davies D, Balkwill F, Burke F (2005) Involvement of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in IFN-gamma-induced apoptosis that are enhanced with cisplatin. Eur J Cancer 41: 1474–1486 - PubMed
-
- Cheng JQ, Jiang X, Fraser M, Li M, Dan HC, Sun M, Tsang BK (2002) Role of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein in chemoresistance in ovarian cancer: possible involvement of the phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt pathway. Drug Resist Updat 5: 131–146 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

