Combined expression of caveolin-1 and an activated AKT/mTOR pathway predicts reduced disease-free survival in clinically confined renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 18283322
- PMCID: PMC2266860
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604243
Combined expression of caveolin-1 and an activated AKT/mTOR pathway predicts reduced disease-free survival in clinically confined renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
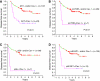
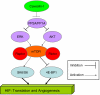
We previously reported that tumour-associated caveolin-1 is a potential biomarker in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), whose overexpression predicts metastasis following surgical resection for clinically confined disease. Much attention has recently focused on the AKT/mTOR pathway in a number of malignancies, including RCC. Since caveolin-1 and the AKT/mTOR signalling cascade are independently shown to be important regulators of tumour angiogenesis, we hypothesised that caveolin-1 interacts with the AKT/mTOR pathway to drive disease progression and metastasis in RCC. The aims of this study were to determine (i) the expression status of the activated AKT/mTOR pathway components (phosphorylated forms) in RCC and (ii) their prognostic value when combined with caveolin-1. Immunohistochemistry for caveolin-1, pAKT, pmTOR, pS6 and p4E-BP1 was performed on tissue microarrays from 174 clinically confined RCCs. Significantly decreased mean disease-free survival was observed when caveolin-1 was coexpressed with either pAKT (2.95 vs 6.14 years), pmTOR (3.17 vs 6.28 years), pS6 (1.45 vs 6.62 years) or p4E-BP1 (2.07 vs 6.09 years) than when neither or any one single biomarker was expressed alone. On multivariate analysis, the covariate of 'caveolin-1/AKT' (neither alone were influential covariates) was a significant influential indicator of poor disease-free survival with a hazard ratio of 2.13 (95% CI: 1.15-3.92), higher than that for vascular invasion. Tumours that coexpressed caveolin-1 and activated mTOR components were more likely to be larger, higher grade and to show vascular invasion. Our results provide the first clinical evidence that caveolin-1 cooperates with an activated AKT/mTOR pathway in cancer and may play an important role in disease progression. We conclude that evaluation of the 'caveolin-1/AKT/mTOR axis' in primary kidney tumours will identify subsets of RCC patients who require greater postoperative surveillance and more intensive treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Altomare DA, Testa JR (2005) Pertubations of the AKT signalling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene 24: 7455–7464 - PubMed
-
- Asano T, Yao Y, Zhu J, Li D, Abbruzzese JL, Reddy SA (2005) The rapamycin analog CCI-779 is a potent inhibitor of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331: 295–302 - PubMed
-
- Averous J, Proud CG (2006) When translation meets transformation: the mTOR story. Oncogene 25: 6423–6435 - PubMed
-
- Carman CV, Lisanti MP, Benovic JL (1999) Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases by caveolin. J Biol Chem 274: 8858–8864 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

