Specific oxidized phospholipids inhibit scavenger receptor bi-mediated selective uptake of cholesteryl esters
- PMID: 18285332
- PMCID: PMC2447666
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M710474200
Specific oxidized phospholipids inhibit scavenger receptor bi-mediated selective uptake of cholesteryl esters
Abstract
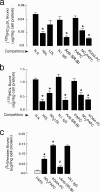
We have recently demonstrated that specific oxidized phospholipids (oxPC(CD36)) accumulate at sites of oxidative stress in vivo such as within atherosclerotic lesions, hyperlipidemic plasma, and plasma with low high-density lipoprotein levels. oxPC(CD36) serve as high affinity ligands for the scavenger receptor CD36, mediate uptake of oxidized low density lipoprotein by macrophages, and promote a pro-thrombotic state via platelet scavenger receptor CD36. We now report that oxPC(CD36) represent ligands for another member of the scavenger receptor class B, type I (SR-BI). oxPC(CD36) prevent binding to SR-BI of its physiological ligand, high density lipoprotein, because of the close proximity of the binding sites for these two ligands on SR-BI. Furthermore, oxPC(CD36) interfere with SR-BI-mediated selective uptake of cholesteryl esters in hepatocytes. Thus, oxidative stress and accumulation of specific oxidized phospholipids in plasma may have an inhibitory effect on reverse cholesterol transport.
Figures
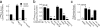

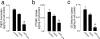
References
-
- Arai, T., Wang, N., Bezouevski, M., Welch, C., and Tall, A. R. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274 2366–2371 - PubMed
-
- Kozarsky, K. F., Donahee, M. H., Glick, J. M., Krieger, M., and Rader, D. J. (2000) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20 721–727 - PubMed
-
- Ueda, Y., Gong, E., Royer, L., Cooper, P. N., Francone, O. L., and Rubin, E. M. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275 20368–20373 - PubMed
-
- Huszar, D., Varban, M. L., Rinninger, F., Feeley, R., Arai, T., Fairchild-Huntress, V., Donovan, M. J., and Tall, A. R. (2000) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20 1068–1073 - PubMed
-
- Acton, S. L., Scherer, P. E., Lodish, H. F., and Krieger, M. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269 21003–21009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

