Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent degeneration, failure, and malignant transformation of the heart in the absence of the von Hippel-Lindau protein
- PMID: 18285456
- PMCID: PMC2423296
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01580-07
Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent degeneration, failure, and malignant transformation of the heart in the absence of the von Hippel-Lindau protein
Abstract
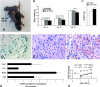
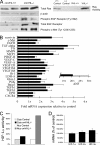
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2alpha regulate the expression of an expansive array of genes associated with cellular responses to hypoxia. Although HIF-regulated genes mediate crucial beneficial short-term biological adaptations, we hypothesized that chronic activation of the HIF pathway in cardiac muscle, as occurs in advanced ischemic heart disease, is detrimental. We generated mice with cardiac myocyte-specific deletion of the von Hippel-Lindau protein (VHL), an essential component of an E3 ubiquitin ligase responsible for suppressing HIF levels during normoxia. These mice were born at expected frequency and thrived until after 3 months postbirth, when they developed severe progressive heart failure and premature death. VHL-null hearts developed lipid accumulation, myofibril rarefaction, altered nuclear morphology, myocyte loss, and fibrosis, features seen for various forms of human heart failure. Further, nearly 50% of VHL(-/-) hearts developed malignant cardiac tumors with features of rhabdomyosarcoma and the capacity to metastasize. As compelling evidence for the mechanistic contribution of HIF-1alpha, the concomitant deletion of VHL and HIF-1alpha in the heart prevented this phenotype and restored normal longevity. These findings strongly suggest that chronic activation of the HIF pathway in ischemic hearts is maladaptive and contributes to cardiac degeneration and progression to heart failure.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha, hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha, and von Hippel-Lindau protein in epithelial ovarian neoplasms and allelic loss of von Hippel-Lindau gene: nuclear expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is an independent prognostic factor in ovarian carcinoma.Hum Pathol. 2007 Sep;38(9):1310-20. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.02.010. Epub 2007 Jun 6. Hum Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17555795
-
Action of hypoxia-inducible factor in liver and kidney from mice with Pax8-rtTA-based deletion of von Hippel-Lindau protein.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2013 Mar;207(3):565-76. doi: 10.1111/apha.12058. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2013. PMID: 23384425
-
Role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha versus HIF-2alpha in the regulation of HIF target genes in response to hypoxia, insulin-like growth factor-I, or loss of von Hippel-Lindau function: implications for targeting the HIF pathway.Cancer Res. 2006 Jun 15;66(12):6264-70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2519. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16778202
-
Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein and hypoxia-inducible factor in kidney cancer.Am J Nephrol. 2004 Jan-Feb;24(1):1-13. doi: 10.1159/000075346. Epub 2003 Dec 3. Am J Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 14654728 Review.
-
The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor, hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) degradation, and cancer pathogenesis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2003 Feb;13(1):83-9. doi: 10.1016/s1044-579x(02)00103-7. Semin Cancer Biol. 2003. PMID: 12507560 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic regulation of HIF-1 signaling in the rhesus monkey heart after ischemic injury.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Sep 11;22(1):407. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02841-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 36089604 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist antibodies activating the Met receptor protect cardiomyoblasts from cobalt chloride-induced apoptosis and autophagy.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Apr 17;5(4):e1185. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.155. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24743740 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of hepatic fibrosis by overexpression of von Hippel-Lindau protein in experimental models of chronic liver disease.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 23;7:41038. doi: 10.1038/srep41038. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28112200 Free PMC article.
-
The von Hippel-Lindau Chuvash mutation in mice alters cardiac substrate and high-energy phosphate metabolism.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;311(3):H759-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00912.2015. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27422990 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue acidosis does not mediate the hypoxia selectivity of [64Cu][Cu(ATSM)] in the isolated perfused rat heart.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 24;9(1):499. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36145-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30679497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altieri, D. C. 2008. Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat. Rev. 861-70. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, M. T., D. Y. Lee, and P. B. Armstrong. 2000. Regulation of proliferation of the fetal myocardium. Dev. Dyn. 219226-236. - PubMed
-
- Burke, B., and C. L. Stewart. 2002. Life at the edge: the nuclear envelope and human disease. Nat. Rev. 3575-585. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J., S. W. Kubalak, and K. R. Chien. 1998. Ventricular muscle-restricted targeting of the RXRalpha gene reveals a non-cell-autonomous requirement in cardiac chamber morphogenesis. Development (Cambridge) 1251943-1949. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
