Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colon: a case report and review of literature
- PMID: 18286700
- PMCID: PMC2689421
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.1137
Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colon: a case report and review of literature
Abstract
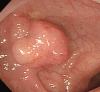
A primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colon is a rare oncologic entity. We herein report a case of such a tumor of the sigmoid colon in a 71-year-old woman who was successfully treated by an endoscopic polypectomy in our hospital. We also reviewed the published reports regarding cases of primary clear cell tumors in the colon.
Figures



References
-
- Hellstrom HR, Fisher ER. Physaliferous Variant of carcinoma of colon. Cancer. 1964;17:259–263. - PubMed
-
- Williams CB, Saunders BP, Talbot IC. Endoscopic management of polypoid early colon cancer. World J Surg. 2000;24:1047–1051. - PubMed
-
- Domoto H, Terahata S, Senoh A, Sato K, Aida S, Tamai S. Clear cell change in colorectal adenomas: its incidence and histological characteristics. Histopathology. 1999;34:250–256. - PubMed
-
- D'Amato A, Nigri G, Pronio A, Montesani C, Ferrazza G, Rusignolo A, Solinas S, Ribotta G. The use of autotransfusion in general surgery. Ann Ital Chir. 2000;71:643–647; discussion 647-648. - PubMed
-
- Tokonabe S, Sugimoto M, Komine Y, Horii H, Matsukuma S. Solitary colonic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma seven years after nephrectomy: a case report. Int J Urol. 1996;3:501–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

