Imaging the impact on cuprate superconductivity of varying the interatomic distances within individual crystal unit cells
- PMID: 18287001
- PMCID: PMC2265138
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706795105
Imaging the impact on cuprate superconductivity of varying the interatomic distances within individual crystal unit cells
Abstract
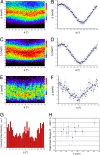
Many theoretical models of high-temperature superconductivity focus only on the doping dependence of the CuO(2)-plane electronic structure. However, such models are manifestly insufficient to explain the strong variations in superconducting critical temperature, T(c), among cuprates that have identical hole density but are crystallographically different outside of the CuO(2) plane. A key challenge, therefore, has been to identify a predominant out-of-plane influence controlling the superconductivity, with much attention focusing on the distance d(A) between the apical oxygen and the planar copper atom. Here we report direct determination of how variations in interatomic distances within individual crystalline unit cells affect the superconducting energy-gap maximum Delta of Bi(2)Sr(2)CaCu(2)O(8+delta). In this material, quasiperiodic variations of unit cell geometry occur in the form of a bulk crystalline "supermodulation." Within each supermodulation period, we find approximately 9 +/- 1% cosinusoidal variation in local Delta that is anticorrelated with the associated d(A) variations. Furthermore, we show that phenomenological consistency would exist between these effects and the random Delta variations found near dopant atoms if the primary effect of the interstitial dopant atom is to displace the apical oxygen so as to diminish d(A) or tilt the CuO(5) pyramid. Thus, we reveal a strong, nonrandom out-of-plane effect on cuprate superconductivity at atomic scale.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Modulated pairs in superconducting cuprates.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Mar 4;105(9):3173-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800433105. Epub 2008 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18305153 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Eisaki H, et al. Effect of chemical inhomogeneity in bismuth-based copper oxide superconductors. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 2004;69 064512.
-
- Ohta Y, Tohyama T, Maekawa S. Apex oxygen and critical temperature in copper oxide superconductors: Universal correlation with the stability of local singlets. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1991;43:2968–2982. - PubMed
-
- Maekawa S, et al. Physics of Transition Metal Oxides. New York: Springer; 2004. Chap 1.
-
- Attfield JP, Kharlanov AL, McAllister JA. Cation effects in doped La2CuO4 superconductors. Nature. 1998;394:157–159.
-
- Fujita K, Noda T, Kojima KM, Eisaki H, Uchida S. Effect of disorder outside the CuO2 planes on Tc of copper oxide superconductors. Phys Rev Lett. 2005;95 097006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

