A virocidal amphipathic {alpha}-helical peptide that inhibits hepatitis C virus infection in vitro
- PMID: 18287023
- PMCID: PMC2268589
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0712380105
A virocidal amphipathic {alpha}-helical peptide that inhibits hepatitis C virus infection in vitro
Abstract
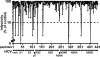
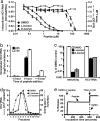
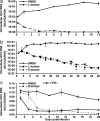
An amphipathic alpha-helical peptide (C5A) derived from the membrane anchor domain of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A protein is virocidal for HCV at submicromolar concentrations in vitro. C5A prevents de novo HCV infection and suppresses ongoing infection by inactivating both extra- and intracellular infectious particles, and it is nontoxic in vitro and in vivo at doses at least 100-fold higher than required for antiviral activity. Mutational analysis indicates that C5A's amphipathic alpha-helical structure is necessary but not sufficient for its virocidal activity, which depends on its amino acid composition but not its primary sequence or chirality. In addition to HCV, C5A inhibits infection by selected flaviviruses, paramyxoviruses, and HIV. These results suggest a model in which C5A destabilizes viral membranes based on their lipid composition, offering a unique therapeutic approach to HCV and other viral infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Francis V. Chisari has a financial interest in Viriome, Inc., which has licensing rights to the information provided in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Hoofnagle JH. Course and outcome of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002;36:S21–S29. - PubMed
-
- Alter HJ, Seeff LB. Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: a perspective on long-term outcome. Semin Liver Dis. 2000;20:17–35. - PubMed
-
- Di Bisceglie AM, McHutchison J, Rice CM. New therapeutic strategies for hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002;35:224–231. - PubMed
-
- Tan SL, Pause A, Shi Y, Sonenberg N. Hepatitis C therapeutics: current status and emerging strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:867–881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

