Validation of virulence and epidemiology DNA microarray for identification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates
- PMID: 18287310
- PMCID: PMC2395118
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02453-07
Validation of virulence and epidemiology DNA microarray for identification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates
Abstract
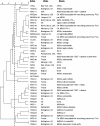
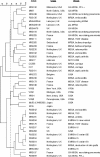
The human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus is isolated and characterized using traditional culture and sensitivity methodologies that are slow and offer limited information on the organism. In contrast, DNA microarray technology can provide detailed, clinically relevant information on the isolate by detecting the presence or absence of a large number of virulence-associated genes simultaneously in a single assay. We have developed and validated a novel, cost-effective multiwell microarray for the identification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus. The array comprises 84 gene targets, including species-specific, antibiotic resistance, toxin, and other virulence-associated genes, and is capable of examining 13 different isolates simultaneously, together with a reference control strain. Analysis of S. aureus isolates whose complete genome sequences have been determined (Mu50, N315, MW2, MRSA252, MSSA476) demonstrated that the array can reliably detect the combination of genes known to be present in these isolates. Characterization of a further 43 S. aureus isolates by the microarray and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis has demonstrated the ability of the array to differentiate between isolates representative of a spectrum of S. aureus types, including methicillin-susceptible, methicillin-resistant, community-acquired, and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus, and to simultaneously detect clinically relevant virulence determinants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream isolates in urban Detroit.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Jul;46(7):2345-52. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00154-08. Epub 2008 May 28. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18508934 Free PMC article.
-
Use of oligoarrays for characterization of community-onset methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Mar;44(3):1040-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.3.1040-1048.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16517892 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization and susceptibility of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates from hospitals and the community in Vladivostok, Russia.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Jun;16(6):575-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02891.x. Epub 2009 Aug 4. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 19681959
-
Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Emerg Infect Dis. 2001 Mar-Apr;7(2):323-6. doi: 10.3201/eid0702.010236. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001. PMID: 11294733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population genetics and the evolution of virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Genet Evol. 2014 Jan;21:554-62. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.04.026. Epub 2013 Apr 27. Infect Genet Evol. 2014. PMID: 23628638 Review.
Cited by
-
Solid and Suspension Microarrays for Microbial Diagnostics.Methods Microbiol. 2015;42:395-431. doi: 10.1016/bs.mim.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 May 14. Methods Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 38620236 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a resistance and virulence gene microarray targeting Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica.J Microbiol Methods. 2010 Jul;82(1):36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2010.03.017. Epub 2010 Mar 31. J Microbiol Methods. 2010. PMID: 20362014 Free PMC article.
-
Early diagnosis of resistant pathogens: how can it improve antimicrobial treatment?Virulence. 2013 Feb 15;4(2):172-84. doi: 10.4161/viru.23326. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Virulence. 2013. PMID: 23302786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a heptaplex PCR assay for identification of Staphylococcus aureus and CoNS with simultaneous detection of virulence and antibiotic resistance genes.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Aug 5;15:157. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0490-9. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26242312 Free PMC article.
-
A community approach to mortality prediction in sepsis via gene expression analysis.Nat Commun. 2018 Feb 15;9(1):694. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03078-2. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29449546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anthony, R. M., A. R. Schuitema, L. Oskam, and P. R. Klatser. 2005. Direct detection of Staphylococcus aureus mRNA using a flow through microarray. J. Microbiol. Methods 6047-54. - PubMed
-
- Brazma, A., P. Hingamp, J. Quackenbush, G. Sherlock, P. Spellman, C. Stoeckert, J. Aach, W. Ansorge, C. A. Ball, H. C. Causton, T. Gaasterland, P. Glenisson, F. C. Holstege, I. F. Kim, V. Markowitz, J. C. Matese, H. Parkinson, A. Robinson, U. Sarkans, S. Schulze-Kremer, J. Stewart, R. Taylor, J. Vilo, and M. Vingron. 2001. Minimum information about a microarray experiment (MIAME)—toward standards for microarray data. Nat. Genet. 29365-371. - PubMed
-
- Corkill, J. E., J. J. Anson, P. Griffiths, and C. A. Hart. 2004. Detection of elements of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome (SCC) in a methicillin-susceptible (mecA gene negative) homologue of a fucidin-resistant MRSA. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 54229-231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

