Breast-feeding patterns, time to initiation, and mortality risk among newborns in southern Nepal
- PMID: 18287373
- PMCID: PMC2366167
- DOI: 10.1093/jn/138.3.599
Breast-feeding patterns, time to initiation, and mortality risk among newborns in southern Nepal
Abstract
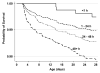
Initiation of breast-feeding within 1 h after birth has been associated with reduced neonatal mortality in a rural Ghanaian population. In South Asia, however, breast-feeding patterns and low birth weight rates differ and this relationship has not been quantified. Data were collected during a community-based randomized trial of the impact of topical chlorhexidine antisepsis interventions on neonatal mortality and morbidity in southern Nepal. In-home visits were conducted on d 1-4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 21, and 28 to collect longitudinal information on timing of initiation and pattern of breast-feeding. Multivariable regression modeling was used to estimate the association between death and breast-feeding initiation time. Analysis was based on 22,838 breast-fed newborns surviving to 48 h. Within 1 h of birth, 3.4% of infants were breast-fed and 56.6% were breast-fed within 24 h of birth. Partially breast-fed infants (72.6%) were at higher mortality risk [relative risk (RR) = 1.77; 95% CI = 1.32-2.39] than those exclusively breast-fed. There was a trend (P = 0.03) toward higher mortality with increasing delay in breast-feeding initiation. Mortality was higher among late (> or = 24 h) compared with early (< 24 h) initiators (RR = 1.41; 95% CI = 1.08-1.86) after adjustment for low birth weight, preterm birth, and other covariates. Improvements in breast-feeding practices in this setting may reduce neonatal mortality substantially. Approximately 7.7 and 19.1% of all neonatal deaths may be avoided with universal initiation of breast-feeding within the first day or hour of life, respectively. Community-based breast-feeding promotion programs should remain a priority, with renewed emphasis on early initiation in addition to exclusiveness and duration of breast-feeding.
Figures
References
-
- Lawn JE, Cousens S, Zupan J. Lancet Neonatal Survival Steering Team. 4 million neonatal deaths: When? Where? Why? Lancet. 2005;365:891–900. - PubMed
-
- Darmstadt GL, Bhutta ZA, Cousens S, Adam T, Walker N, de Bernis L, Lancet Neonatal Survival Steering Team Evidence-based, cost-effective interventions: how many newborn babies can we save? Lancet. 2005;365:977–88. - PubMed
-
- Mullany LC, Darmstadt GL, Khatry SK, Katz J, LeClerq SC, Shrestha S, Adhikari R, Tielsch JM. Topical applications of chlorhexidine to the umbilical cord for prevention of omphalitis and neonatal mortality in southern Nepal: a community-based, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet. 2006;367:910–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klemm RD, Labrique A, Christian P, Rashid R, Shamim AA, Katz J. Micronutrient Forum Abstracts. Istanbul, Turkey: Apr 16-18, 2007. Efficacy of newborn vitamin A supplementation in reducing infant mortality in rural Bangladesh: the JiVitA-2 trial.