Effect of montelukast on platelet activating factor- and tachykinin induced mucus secretion in the rat
- PMID: 18289370
- PMCID: PMC2278150
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6673-3-5
Effect of montelukast on platelet activating factor- and tachykinin induced mucus secretion in the rat
Abstract
Background: Platelet activating factor and tachykinins (substance P, neurokinin A, neurokinin B) are important mediators contributing to increased airway secretion in the context of different types of respiratory diseases including acute and chronic asthma. Leukotriene receptor antagonists are recommended as add-on therapy for this disease. The cys-leukotriene-1 receptor antagonist montelukast has been used in clinical asthma therapy during the last years. Besides its inhibitory action on bronchoconstriction, only little is known about its effects on airway secretions. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of montelukast on platelet activating factor- and tachykinin induced tracheal secretory activity.
Methods: The effects of montelukast on platelet activating factor- and tachykinin induced tracheal secretory activity in the rat were assessed by quantification of secreted 35SO4 labelled mucus macromolecules using the modified Ussing chamber technique.
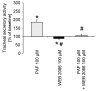
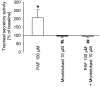
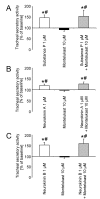
Results: Platelet activating factor potently stimulated airway secretion, which was completely inhibited by the platelet activating factor receptor antagonist WEB 2086 and montelukast. In contrast, montelukast had no effect on tachykinin induced tracheal secretory activity.
Conclusion: Cys-leukotriene-1 receptor antagonism by montelukast reverses the secretagogue properties of platelet activating factor to the same degree as the specific platelet activating factor antagonist WEB 2086 but has no influence on treacheal secretion elicited by tachykinins. These results suggest a role of montelukast in the signal transduction pathway of platelet activating factor induced secretory activity of the airways and may further explain the beneficial properties of cys-leukotriene-1 receptor antagonists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
'Sensory-efferent' neural control of mucus secretion: characterization using tachykinin receptor antagonists in ferret trachea in vitro.Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1183-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17122.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7889271 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of two novel tachykinin antagonists, FK224 and FK888, on neurogenic airway plasma exudation, bronchoconstriction and systemic hypotension in guinea-pigs in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):844-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12888.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 7682142 Free PMC article.
-
The cysteinyl-leukotriene-1 receptor antagonist zafirlukast is a potent secretagogue in rat and human airways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec 19;527(1-3):150-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.08.064. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16310765
-
Sensory neuropeptides and the human lower airways: present state and future directions.Eur Respir J. 1994 Jun;7(6):1161-71. Eur Respir J. 1994. PMID: 7925887 Review.
-
The leukotriene receptor antagonist montelukast and its possible role in the cardiovascular field.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jul;73(7):799-809. doi: 10.1007/s00228-017-2242-2. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28374082 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of montelukast for uremic pruritus in hemodialysis patients: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 13;99(46):e23229. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023229. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33181709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rogers DF. Physiology of airway mucus secretion and pathophysiology of hypersecretion. Respir Care. 2007;52:1134–46. discussion 1146-9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

