Currying favor for the heart
- PMID: 18292806
- PMCID: PMC2248428
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI34650
Currying favor for the heart
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2009 Jul;119(7):2113
Abstract
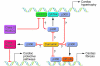
Curcumin, a commonly available spice and alternative medicine, has been tested in the laboratory and the clinic for activity against a wide range of diseases. It is thought to possess antiinflammatory and antioxidant activities and may also function to inhibit histone acetyl transferases, which activate gene expression via chromatin remodeling. Two reports in this issue of the JCI, by Morimoto et al. and Li et al., suggest that curcumin may inhibit cardiac hypertrophy in rodent models and provide beneficial effects after myocardial infarction or in the setting of hypertension (see the related articles beginning on pages 868 and 879, respectively). These results will spur further mechanistic inquiry into the role of chromatin remodeling in the regulation of cardiac homeostasis.
Figures
Comment on
-
Curcumin prevents and reverses murine cardiac hypertrophy.J Clin Invest. 2008 Mar;118(3):879-93. doi: 10.1172/JCI32865. J Clin Invest. 2008. Retraction in: J Clin Invest. 2009 Jul;119(7):2113. doi: 10.1172/jci32865r1. PMID: 18292803 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The dietary compound curcumin inhibits p300 histone acetyltransferase activity and prevents heart failure in rats.J Clin Invest. 2008 Mar;118(3):868-78. doi: 10.1172/JCI33160. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18292809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backs J., Olson E.N. Control of cardiac growth by histone acetylation/deacetylation. Circ. Res. 2006;98:15–24. - PubMed
-
- Kelly W.K., Marks P.A. Drug insight: Histone deacetylase inhibitors — development of the new targeted anticancer agent suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005;2:150–157. - PubMed
-
- Trivedi C.M., et al. Hdac2 regulates the cardiac hypertrophic response by modulating Gsk3 beta activity. Nat. Med. 2007;13:324–331. - PubMed

