Direct assay of enzymes in heme biosynthesis for the detection of porphyrias by tandem mass spectrometry. Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase and coproporphyrinogen III oxidase
- PMID: 18294003
- PMCID: PMC2515868
- DOI: 10.1021/ac702130n
Direct assay of enzymes in heme biosynthesis for the detection of porphyrias by tandem mass spectrometry. Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase and coproporphyrinogen III oxidase
Abstract
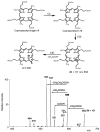
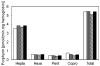
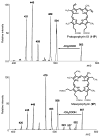
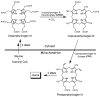
We report new assays of enzymes uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase (UROD) and coproporphyrinogen III oxidase (CPO) in the heme biosynthetic pathway. The assays were developed for use in clinical diagnostics of inherited disorders porphyria cutanea tarda and hereditary coproporphyria, respectively. Electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry is used to monitor the decarboxylation of pentaporphyrinogen I or uroporphyrinogen III catalyzed by UROD and to determine the enzyme activity in human erythrocytes by measuring the production of coproporphyrinogen I or III. The Km value for pentaporphyrinogen I was measured as 0.17 +/- 0.03 microM. A mass spectrometric assay was also developed for the two-step decarboxylative oxidation of coproporphyrinogen III to protoporphyrinogen IX catalyzed by CPO in mitochondria from human lymphocytes (Km = 0.066 +/- 0.009 microM). The assays show good reproducibility, use simple workup by liquid-liquid extraction of enzymatic products, and employ commercially available substrates and internal standards.
Figures



References
-
- Kappas A, Sassa S, Galbraith RA, Nordmann Y. The Porphyrias. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease. 7. Chapter 66. II. McGraw-Hill; New York: 1995. pp. 2103–2159.
-
- Brodie MJ, Thompson GG, Moore MR, Beattie AD, Goldberg A. Quant J Med. 1977;46:229–241. - PubMed
-
- Kuhnel A, Gross U, Doss MO. Clin Biochem. 2000;33:465–473. - PubMed
-
- Jones MA, Thientanavanich P, Anderson MD, Lash TD. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 2003;55:241–249. - PubMed
-
- Francis JE, Smith AG. Anal Biochem. 1984;138:404–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

