Inflammation and cancer: role of nuclear factor-kappaB activation
- PMID: 18294278
- PMCID: PMC11159293
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00763.x
Inflammation and cancer: role of nuclear factor-kappaB activation
Abstract
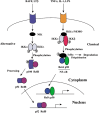
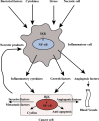
It has been thought that there is a strong relationship between inflammation and carcinogenesis so that the development of cancer occurs with chronic inflammation in many organs. An in-depth understanding of the mechanism by which inflammation can lead to carcinogenesis may enable the development of drugs targeted at important molecules, providing a powerful tool for preventing cancer development. In this review, we focused on a signal transduction system, the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway, which is thought to play a role in the process leading from inflammation to carcinogenesis, and may thus serve as a candidate for targeted intervention.
Figures


References
-
- Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2002; 16 (217–26): 29; discussion 30–2. - PubMed
-
- Nomura A, Stemmermann GN, Chyou PH, Kato I, Perez‐Perez GI, Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 1132–6. - PubMed
-
- Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology 2004; 127: S35–50. - PubMed
-
- Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S et al . Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 784–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

