The recovery time-course of CYP3A after induction by St John's wort administration
- PMID: 18294328
- PMCID: PMC2432480
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03120.x
The recovery time-course of CYP3A after induction by St John's wort administration
Abstract
What is already known about this subject: St John's wort causes the induction of CYP3A. Little is known about how long the effect remains after cessation of St John's wort.
What this study adds: The in vivo CYP3A activity returns progressively to the basal level approximately 1 week after cessation of St John's wort administration
Aims: To examine the recovery time course of CYP3A after enzyme induction by St John's wort administration.
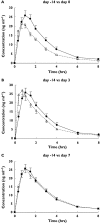
Methods: The subjects were 12 healthy men, aged 20-33 years. On the first day, they received an oral dose of midazolam 5 mg without St John's wort (day -14). From the next day, they took St John's wort for 14 days. On the last day of St John's wort treatment (day 0) and 3 and 7 days after completion of St John's wort treatment (days 3 and 7), they received the same dose of midazolam. On each day, blood samples were obtained until 8 h after midazolam administration. Plasma concentrations of midazolam were measured by HPLC. Pharmacokinetic parameters of midazolam were determined using noncompartmental analysis.
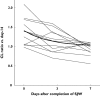
Results: Apparent oral clearance of midazolam was significantly increased after St John's wort administration from 65.3 +/- 8.4 l h(-1) (day -14) to 86.8 +/- 17.3 l h(-1) (day 0). It returned to the control level 7 days after the completion of St John's wort (day 7, 59.7 +/- 3.8 l h(-1)). No significant difference in the elimination half-life between the four periods of the study was observed. The changes in apparent oral clearance after St John's wort discontinuation indicated that CYP3A activity recovers from enzyme induction with an estimated half-life of 46.2 h.
Conclusions: CYP3A activity induced by St John's wort administration progressively returns to the basal level after approximately 1 week. This finding may provide useful information to avoid clinically significant interactions of St John's wort with CYP3A substrates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) on human cytochrome P450 activity.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Oct;70(4):317-26. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11673747 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of simultaneous induction and inhibition of CYP3A by St John's Wort and ritonavir on CYP3A activity.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Feb;87(2):191-6. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2009.206. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 19924124 Clinical Trial.
-
The interaction between St John's wort and an oral contraceptive.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Dec;74(6):525-35. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2003.08.009. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 14663455 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic interactions of drugs with St John's wort.J Psychopharmacol. 2004 Jun;18(2):262-76. doi: 10.1177/0269881104042632. J Psychopharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15260917 Review.
-
Understanding drug interactions with St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L.): impact of hyperforin content.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;71(1):129-138. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12858. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29411879 Review.
Cited by
-
Herb-drug interactions with St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum): an update on clinical observations.AAPS J. 2009 Dec;11(4):710-27. doi: 10.1208/s12248-009-9146-8. Epub 2009 Oct 27. AAPS J. 2009. PMID: 19859815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The JAK1 Inhibitor Upadacitinib Has No Effect on the Pharmacokinetics of Levonorgestrel and Ethinylestradiol: A Study in Healthy Female Subjects.J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Apr;59(4):510-516. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1350. Epub 2018 Nov 30. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30500075 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alternatives to rifampicin: A review and perspectives on the choice of strong CYP3A inducers for clinical drug-drug interaction studies.Clin Transl Sci. 2022 Sep;15(9):2075-2095. doi: 10.1111/cts.13357. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Clin Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35722783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug interactions with herbal medicines.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012 Feb 1;51(2):77-104. doi: 10.2165/11597910-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012. PMID: 22257149 Review.
-
Utilization of a Human Liver Tissue Chip for Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme Induction Studies of Perpetrator and Victim Drugs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 22:2024.07.17.603946. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.17.603946. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Drug Metab Dispos. 2025 Jan;53(1):100004. doi: 10.1124/dmd.124.001497. PMID: 39091853 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Roby CA, Anderson GD, Kantor E, Dryer DA, Burstein AH. St John's Wort: effect on CYP3A4 activity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000;67:451–7. - PubMed
-
- Greeson JM, Sanford B, Monti DA. St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum): a review of the current pharmacological, toxicological, and clinical literature. Psychopharmacology. 2001;153:402–14. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Gorski JC, Hamman MA, Huang SM, Lesko LJ, Hall SD. The effects of St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) on human cytochrome P450 activity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;70:317–26. - PubMed
-
- Markowitz JS, Donovan JL, DeVane CL, Taylor RM, Ruan Y, Wang JS, Chavin KD. Effect of St John's wort on drug metabolism by induction of cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme. JAMA. 2003;290:1500–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

