Comparison of risk stratification schemes to predict thromboembolism in people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 18294564
- PMCID: PMC3534960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.09.065
Comparison of risk stratification schemes to predict thromboembolism in people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Objectives: We assessed 5 risk stratification schemes for their ability to predict atrial fibrillation (AF)-related thromboembolism in a large community-based cohort.
Background: Risk schemes can help target anticoagulant therapy for patients at highest risk for AF-related thromboembolism. We tested the predictive ability of 5 risk schemes: the Atrial Fibrillation Investigators, Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation, CHADS(2) (Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age >or= 75 years, Diabetes mellitus, and prior Stroke or transient ischemic attack) index, Framingham score, and the 7th American College of Chest Physicians Guidelines.
Methods: We followed a cohort of 13,559 adults with AF for a median of 6.0 years. Among non-warfarin users, we identified incident thromboembolism (ischemic stroke or peripheral embolism) and risk factors from clinical databases. Each scheme was divided into low, intermediate, and high predicted risk categories and applied to the cohort. Annualized thromboembolism rates and c-statistics (to assess discrimination) were calculated for each risk scheme.
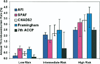
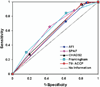
Results: We identified 685 validated thromboembolic events that occurred during 32,721 person-years off warfarin therapy. The risk schemes had only fair discriminating ability, with c-statistics ranging from 0.56 to 0.62. The proportion of patients assigned to individual risk categories varied widely across the schemes. The proportion categorized as low risk ranged from 11.7% to 37.1% across schemes, and the proportion considered high risk ranged from 16.4% to 80.4%.
Conclusions: Current risk schemes have comparable, but only limited, overall ability to predict thromboembolism in persons with AF. Recommendations for antithrombotic therapy may vary widely depending on which scheme is applied for individual patients. Better risk stratification is crucially needed to improve selection of AF patients for anticoagulant therapy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Predicting thromboembolism and selecting patients for anticoagulant therapy in atrial fibrillation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Feb 26;51(8):816-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.10.045. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18294565 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation: a major contributor to stroke in the elderly. The Framingham Study. Arch Intern Med. 1987;147:1561–1564. - PubMed
-
- Atrial Fibrillation Investigators. Risk factors for stroke and efficacy of antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation: analysis of pooled data from 5 randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154:1449–1457. - PubMed
-
- Gage BF, van Walraven C, Pearce L, et al. Selecting patients with atrial fibrillation for anticoagulation: stroke risk stratification in patients taking aspirin. Circulation. 2004;110:2287–2292. - PubMed
-
- Pearce L, Hart R, Halperin J. Assessment of three schemes for stratifying stroke risk in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Am J Med. 2000;109:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, et al. Implications of stroke risk criteria on the anticoagulation decision in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: the Anticoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) study. Circulation. 2000;102:11–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

