An embarrassment of riches: the enzymology of RNA modification
- PMID: 18294973
- PMCID: PMC2430154
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.01.041
An embarrassment of riches: the enzymology of RNA modification
Abstract
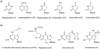
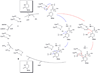
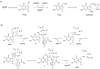
The maturation of transfer RNA (tRNA) involves extensive chemical modification of the constituent nucleosides and results in the introduction of significant chemical diversity to tRNA. Many of the pathways to these modified nucleosides are characterized by chemically complex transformations, some of which are unprecedented in other areas of biology. To illustrate the scope of the field, recent progress in understanding the enzymology leading to the formation of two distinct classes of modified nucleosides, the thiouridines and queuosine, a 7-deazaguanosine, is reviewed. In particular, recent data validating the involvement of several proposed intermediates in the formation of thiouridines are discussed, including two key enzyme intermediates and the activated tRNA intermediate. The discovery and mechanistic characterization of a new enzyme activity in the queuosine pathway is discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Hopper AK, Phizicky EM. tRNA transfers to the limelight. Genes Dev. 2003;17:162–180. - PubMed
-
-
* Dunin-Horkawicz S, Czerwoniec A, Gajda MJ, Feder M, Grosjean H, Bujnicki JM. MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:D145–D149. An excellent database that brings together the structures, biosynthetic pathways, and enzymes of RNA modification, as well as RNA sequences.
-
-
- Bjork GR. Biosynthesis and Function of Modified Nucleosides. In: Soll D, RajBhandary UL, editors. tRNA: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Function. ASM Press; 1995. pp. 165–206.
-
- de Crécy-Lagard V. Bioinformatics leads the path to the identification of missing tRNA modification genes. In: Bujnicki JM, editor. Practical Bioinformatics. vol 15. Springer-Verlag; 2004. pp. 169–190.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

