Croup
- PMID: 18295000
- PMCID: PMC7138055
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60170-1
Croup
Abstract
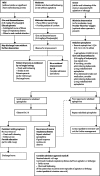
Most children who present with acute onset of barky cough, stridor, and chest-wall indrawing have croup. A careful history and physical examination is the best method to confirm the diagnosis and to rule out potentially serious alternative disorders such as bacterial tracheitis and other rare causes of upper-airway obstruction. Epinephrine delivered via a nebuliser is effective for temporary relief of symptoms of airway obstruction. Corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment, and benefit is seen in children with all levels of severity of croup, including mild cases.
Figures
References
-
- Stool S. Croup syndrome: historical perspective. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988;7:S157–S161. - PubMed
-
- Denny F, Murphy T, Clyde W, Collier A, Henderson F. Croup: an 11-year study in a pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 1983;71:871–876. - PubMed
-
- Marx A, Torok T, Holman R, Clarke M, Anderson L. Pediatric hospitalizations for croup (laryngotracheobronchitis): biennial increases associated with human parainfluenza virus 1 epidemics. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:1423–1427. - PubMed
-
- Johnson D, Williamson J. Croup: duration of symptoms and impact on family functioning. Pediatr Research. 2001;49:83A.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical