Effect of AZT on thymidine phosphorylation in cultured H9c2, U-937, and Raji cell lines
- PMID: 18295188
- PMCID: PMC2364649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.01.006
Effect of AZT on thymidine phosphorylation in cultured H9c2, U-937, and Raji cell lines
Abstract
3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) has been shown to be a potent inhibitor of thymidine kinase 2 in work from this laboratory. Inhibition results in decreased salvage of thymidine to TTP, which may lead to depletion of the TTP pool and result in the mitochondrial dysfunction and mt-DNA depletion observed with AZT toxicity. The effect of AZT on thymidine phosphorylation in growing cells expressing thymidine kinase 1 has not been shown. Three cell lines were used in these experiments: H9c2, derived from rat cardiomyoblasts; U-937, derived from human monocytes; and Raji, derived from human lymphoblasts. AZT inhibited growth in a concentration-dependent manner in U-937 cells, but not the other cell lines. The phosphorylation of [3H]-thymidine or [3H]-AZT was determined during log growth. All cell lines salvaged and phosphorylated thymidine to TTP, with TTP the major product. The U-937 cells had a much more active salvage pathway than the other cells. All cell lines phosphorylated AZT to the triphosphate, but the major product was AZTMP. The AZT inhibition of growth of the U-937 cells did not correlate with levels of the phosphorylated AZT. In contrast, pro-drug AZT was shown to inhibit thymidine phosphorylation in all lines with 50% inhibition concentrations (IC50) ranging from 4.4 to 21.9muM. Since the U-937 cells expressed higher activity of the salvage pathway than the other cell lines, the U-937 cells may rely more heavily on the salvage pathway for TTP synthesis, accounting for AZT inhibition of growth.
Figures

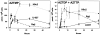


Similar articles
-
Zidovudine inhibits thymidine phosphorylation in the isolated perfused rat heart.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Apr;51(4):1142-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01227-06. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17220403 Free PMC article.
-
3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) inhibits thymidine phosphorylation in isolated rat liver mitochondria: a possible mechanism of AZT hepatotoxicity.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Apr 28;71(9):1342-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.01.003. Epub 2006 Feb 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16472780 Free PMC article.
-
3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) is a competitive inhibitor of thymidine phosphorylation in isolated rat heart and liver mitochondria.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Jul 14;72(2):239-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.04.004. Epub 2006 Apr 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16720018 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of thymidine and AZT in heart mitochondria: elucidation of a novel mechanism of AZT cardiotoxicity.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2004;4(2):155-67. doi: 10.1385/ct:4:2:155. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 15371631 Free PMC article.
-
A critical analysis of the pharmacology of AZT and its use in AIDS.Curr Med Res Opin. 1999;15 Suppl 1:S1-45. doi: 10.1185/03007999909114096. Curr Med Res Opin. 1999. PMID: 11594171 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of heterochromatin and retrotransposon silencing as determinants in oocyte aging.Aging Cell. 2022 Mar;21(3):e13568. doi: 10.1111/acel.13568. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Aging Cell. 2022. PMID: 35166017 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of remdesivir to affect function, metabolism and proliferation of cardiac and kidney cells in vitro.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Aug;96(8):2341-2360. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03306-1. Epub 2022 May 17. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35579693 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism of deoxypyrimidines and deoxypyrimidine antiviral analogs in isolated brain mitochondria.J Neurochem. 2012 Jul;122(1):126-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07765.x. Epub 2012 May 21. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22530558 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier efflux transport of pyrimidine nucleosides and nucleobases in the rat.Neurochem Res. 2009 Mar;34(3):566-73. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9823-5. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Neurochem Res. 2009. PMID: 18751895
-
A novel (11)C-labeled thymidine analog, [(11)C]AZT, for tumor imaging by positron emission tomography.EJNMMI Res. 2015 Dec;5(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13550-015-0124-0. Epub 2015 Sep 4. EJNMMI Res. 2015. PMID: 26337804 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

