Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced transcellular transport of HIV-1 across the blood-brain barrier is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
- PMID: 18295207
- PMCID: PMC2385783
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.12.028
Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced transcellular transport of HIV-1 across the blood-brain barrier is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
Abstract
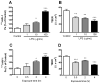
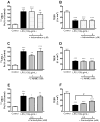
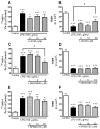
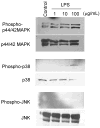
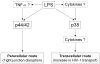
Chronic systemic inflammation in the late stage of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) infection could increase neuroinvasion of infected monocytes and cell-free virus, causing an aggravation of neurological disorders in AIDS patients. We previously showed that the peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) enhanced the uptake across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) of the HIV-1 viral protein gp120. Brain microvessel endothelial cells are targets of LPS. Here, we investigated whether the direct interaction between LPS and the BBB also affected HIV-1 transport using primary mouse brain microvessel endothelial cells (BMECs). LPS produced a dose (1-100 microg/mL)- and time (0.5-4 h)-dependent increase in HIV-1 transport and a decrease in transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER). Whereas indomethacin (cyclooxygenase inhibitor) and L-NAME (NO synthase inhibitor) did not affect the LPS-induced changes in HIV-1 transport or TEER, pentoxifylline (TNF-alpha inhibitor) attenuated the decrease in TEER induced by LPS, but not the LPS-induced increase in HIV-1 transport. LPS also increased the phosphorylation of p44/42 MAPK and p38 MAPK but not that of JNK. U0126 (p44/42 MAPK inhibitor) and SP600125 (JNK inhibitor) did not inhibit the LPS-induced increase in HIV-1 transport although U0126 attenuated the reduction in TEER. SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) inhibited the LPS-induced increase in HIV-1 transport without affecting TEER. Thus, LPS-enhanced HIV-1 transport is independent of changes in TEER and so is attributed to increased transcellular trafficking of HIV-1 across the BBB. These results show that LPS increases HIV-1 transcellular transport across the BBB by a pathway that is mediated by p38 MAPK phosphorylation in BMECs.
Figures
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Alonso K, Pontiggia P, Medenica R, Rizzo S. Cytokine patterns in adults with AIDS. Immunol Invest. 1997;26:341–350. - PubMed
-
- András IE, Pu H, Deli MA, Nath A, Hennig B, Toborek M. HIV-1 Tat protein alters tight junction protein expression and distribution in cultured brain endothelial cells. J Neurosci Res. 2003;74:255–265. - PubMed
-
- András IE, Pu H, Tian J, Deli MA, Nath A, Hennig B, Toborek M. Signaling mechanisms of HIV-1 Tat-induced alterations of claudin-5 expression in brain endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25:1159–1170. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Akerstrom V, Kastin AJ. Adsorptive endocytosis mediates the passage of HIV-1 across the blood-brain barrier: evidence for a post-internalization coreceptor. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:533–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

