In vitro and in vivo characterization of retinoid synthesis from beta-carotene
- PMID: 18295589
- PMCID: PMC2587144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.02.010
In vitro and in vivo characterization of retinoid synthesis from beta-carotene
Abstract
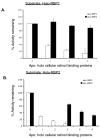
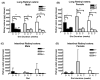
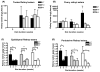
Retinoids are indispensable for the health of mammals, which cannot synthesize retinoids de novo. Retinoids are derived from dietary provitamin A carotenoids, like beta-carotene, through the actions of beta-carotene-15,15'-monooxygenase (BCMO1). As the substrates for retinoid-metabolizing enzymes are water insoluble, they must be transported intracellularly bound to cellular retinol-binding proteins. Our studies suggest that cellular retinol-binding protein, type I (RBP1) acts as an intracellular sensor of retinoid status that, when present as apo-RBP1, stimulates BCMO1 activity and the conversion of carotenoids to retinoids. Cellular retinol-binding protein, type II (RBP2), which is 56% identical to RBP1 does not influence BCMO1 activity. Studies of mice lacking BCMO1 demonstrate that BCMO1 is responsible for metabolically limiting the amount of intact beta-carotene that can be absorbed by mice from their diet. Our studies provide new insights into the regulation of BCMO1 activity and the physiological role of BCMO1 in living organisms.
Figures
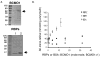



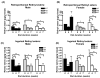
References
-
- Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS. The Retinoids : Biology, Chemistry, and Medicine. 2. Raven Press; New York: 1994.
-
- Chambon P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. Faseb J. 1996;10:940–954. - PubMed
-
- Evans RM. The nuclear receptor superfamily: a rosetta stone for physiology. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19:1429–1438. - PubMed
-
- Pennimpede T, Cameron D, Petkovich M. Regulation of murine embryonic patterning and morphogenesis by retinoic acid signaling. Adv Dev Biol. 2006;16:65–104.
-
- Balmer JE, Blomhoff R. Gene expression regulation by retinoic acid. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:1773–1808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

