Retinal isoforms of inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase type 1 are poor nucleic acid binding proteins
- PMID: 18295591
- PMCID: PMC2366119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.02.012
Retinal isoforms of inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase type 1 are poor nucleic acid binding proteins
Abstract
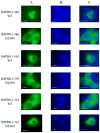
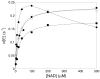
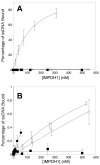
The RP 10 form of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (adRP) is caused by mutations in the widely expressed protein inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase type 1 (IMPDH1). These mutations have no effect on the enzymatic activity of IMPDH1, but do perturb the association of IMPDH1 with nucleic acids. Two newly discovered retinal-specific isoforms, IMPDH1(546) and IMPDH1(595), may provide the key to the photoreceptor specificity of disease [S.J. Bowne, Q. Liu, L.S. Sullivan, J. Zhu, C.J. Spellicy, C.B. Rickman, E.A. Pierce, S.P. Daiger, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 47 (2006) 3754-3765]. Here we express and characterize the normal IMPDH1(546) and IMPDH1(595), together with their adRP-linked variants, D226N. The enzymatic activity of the purified IMPDH1(546), IMPDH1(595) and the D226N variants is indistinguishable from the canonical form. The intracellular distribution of IMPDH1(546) and IMPDH1(595) is also similar to the canonical IMPDH1 and unaffected by the D226N mutation. However, unlike the canonical IMPDH1, the retinal specific isoforms do not bind significant fractions of a random pool of oligonucleotides. This observation indicates that the C-terminal extension unique to the retinal isoforms blocks the nucleic acid binding site of IMPDH1, and thus uniquely regulates protein function within photoreceptors.
Figures

References
-
- Heckenlively JR, Daiger SP. Principals and Practices of Medical Genetics. In: Rimoin DI, Connor JM, Pyeritz RE, editors. Churchill Livingston. New York: 2001; 2255. p. 2576.
-
- Chang GQ, Hao Y, Wong F. Neuron. 1993;11:595–605. - PubMed
-
- Kennan A, Aherne A, Palfi A, Humphries M, McKee A, Stitt A, Simpson DA, Demtroder K, Orntoft T, Ayuso C, Kenna PF, Farrar GJ, Humphries P. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:547–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

