Identification of CKAP4/p63 as a major substrate of the palmitoyl acyltransferase DHHC2, a putative tumor suppressor, using a novel proteomics method
- PMID: 18296695
- PMCID: PMC2493380
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M800069-MCP200
Identification of CKAP4/p63 as a major substrate of the palmitoyl acyltransferase DHHC2, a putative tumor suppressor, using a novel proteomics method
Abstract
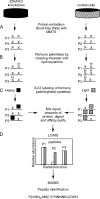
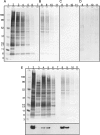
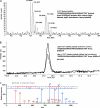
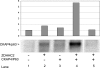
Protein palmitoylation is the post-translational addition of the 16-carbon fatty acid palmitate to specific cysteine residues by a labile thioester linkage. Palmitoylation is mediated by a family of at least 23 palmitoyl acyltransferases (PATs) characterized by an Asp-His-His-Cys (DHHC) motif. Many palmitoylated proteins have been identified, but PAT-substrate relationships are mostly unknown. Here we present a method called palmitoyl-cysteine isolation capture and analysis (or PICA) to identify PAT-substrate relationships in a living vertebrate system and demonstrate its effectiveness by identifying CKAP4/p63 as a substrate of DHHC2, a putative tumor suppressor.
Figures
References
-
- Fukata, M., Fukata, Y., Adesnik, H., Nicoll, R. A., and Bredt, D. S. ( 2004) Identification of PSD-95 palmitoylating enzymes. Neuron 44, 987–996 - PubMed
-
- Drisdel, R. C., and Green, W. N. ( 2004) Labeling and quantifying sites of protein palmitoylation. BioTechniques 36, 276–285 - PubMed
-
- Oyama, T., Miyoshi, Y., Koyama, K., Nakagawa, H., Yamori, T., Ito, T., Matsuda, H., Arakawa, H., and Nakamura, Y. ( 2000) Isolation of a novel gene on 8p21.3-22 whose expression is reduced significantly in human colorectal cancers with liver metastasis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 29, 9–15 - PubMed
-
- Wong, M. L., and Medrano, J. F. ( 2005) Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation. BioTechniques 39, 75–85 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

