Golgi cisternal unstacking stimulates COPI vesicle budding and protein transport
- PMID: 18297130
- PMCID: PMC2249924
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001647
Golgi cisternal unstacking stimulates COPI vesicle budding and protein transport
Abstract
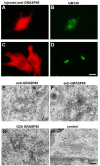
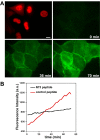
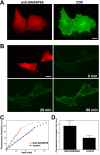
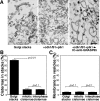
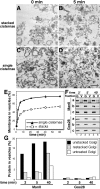
The Golgi apparatus in mammalian cells is composed of flattened cisternae that are densely packed to form stacks. We have used the Golgi stacking protein GRASP65 as a tool to modify the stacking state of Golgi cisternae. We established an assay to measure protein transport to the cell surface in post-mitotic cells in which the Golgi was unstacked. Cells with an unstacked Golgi showed a higher transport rate compared to cells with stacked Golgi membranes. Vesicle budding from unstacked cisternae in vitro was significantly increased compared to stacked membranes. These results suggest that Golgi cisternal stacking can directly regulate vesicle formation and thus the rate of protein transport through the Golgi. The results further suggest that at the onset of mitosis, unstacking of cisternae allows extensive and rapid vesiculation of the Golgi in preparation for its subsequent partitioning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mironov AA, Beznoussenko GV, Polishchuk RS, Trucco A. Intra-Golgi transport: a way to a new paradigm? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1744:340–350. - PubMed
-
- Trucco A, Polishchuk RS, Martella O, Di Pentima A, Fusella A, et al. Secretory traffic triggers the formation of tubular continuities across Golgi sub-compartments. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:1071–1081. - PubMed
-
- Elsner M, Hashimoto H, Nilsson T. Cisternal maturation and vesicle transport: join the band wagon! (Review). Mol Membr Biol. 2003;20:221–229. - PubMed
-
- Losev E, Reinke CA, Jellen J, Strongin DE, Bevis BJ, et al. Golgi maturation visualized in living yeast. Nature. 2006;441:1002–1006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

