Mice lacking alpha-tocopherol transfer protein gene have severe alpha-tocopherol deficiency in multiple regions of the central nervous system
- PMID: 18299118
- PMCID: PMC2832471
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.044
Mice lacking alpha-tocopherol transfer protein gene have severe alpha-tocopherol deficiency in multiple regions of the central nervous system
Abstract
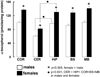
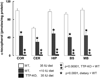
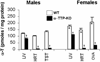
Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency is caused by mutations in alpha-tocopherol transfer protein (alpha-TTP) gene and it can be experimentally generated in mice by alpha-TTP gene inactivation (alpha-TTP-KO). This study compared alpha-tocopherol (alpha-T) concentrations of five brain regions and of four peripheral organs from 5 months old, male and female, wild-type (WT) and alpha-TTP-KO mice. All brain regions of female WT mice contained significantly higher alpha-T than those from WT males. alpha-T concentration in the cerebellum was significantly lower than that in other brain regions of WT mice. These sex and regional differences in brain alpha-T concentrations do not appear to be determined by alpha-TTP expression which was undetectable in all brain regions. All the brain regions of alpha-TTP-KO mice were severely depleted in alpha-T. The concentration of another endogenous antioxidant, total glutathione, was unaffected by gender but was decreased slightly but significantly in most brain regions of alpha-TTP-KO mice. The results show that both gender and the hepatic alpha-TTP, but not brain alpha-TTP gene expression are important in determining alpha-T concentrations within the brain. Interestingly, functional abnormality (ataxia) develops only very late in alpha-TTP-KO mice in spite of the severe alpha-tocopherol deficiency in the brain starting at an early age.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Vitamin E is essential for Purkinje neuron integrity.Neuroscience. 2014 Feb 28;260:120-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24342566 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of long-term vitamin E insufficiency or excess on bone mass, density, and microarchitecture in rodents.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:1209-1214. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 24051180 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed-onset ataxia in mice lacking alpha -tocopherol transfer protein: model for neuronal degeneration caused by chronic oxidative stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 18;98(26):15185-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261456098. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11752462 Free PMC article.
-
α-Tocopherol transfer protein (α-TTP).Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Nov 20;176:162-175. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.09.021. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34563650 Review.
-
Vitamin E trafficking.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Dec;1031:1-12. doi: 10.1196/annals.1331.001. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15753129 Review.
Cited by
-
The detection of age-, gender-, and region-specific changes in mouse brain tocopherol levels via the application of different validated HPLC methods.Neurochem Res. 2018 Nov;43(11):2081-2091. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2630-8. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 30194607
-
The neuropathobiology of multiple sclerosis.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2024 Jul;25(7):493-513. doi: 10.1038/s41583-024-00823-z. Epub 2024 May 24. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38789516 Review.
-
Vitamin E Supplementation Reduces Cellular Loss in the Brain of a Premature Aging Mouse Model.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2017;4(4):226-235. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2017.30. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 29181487 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Vitamin E Status Dictates Oxidative Stress Outcomes by Modulating Effects of Fish Oil Supplementation in Alzheimer Disease Model APPswe/PS1dE9 Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Dec;55(12):9204-9219. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1060-6. Epub 2018 Apr 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29656360
-
Why Have Clinical Trials of Antioxidants to Prevent Neurodegeneration Failed? - A Cellular Investigation of Novel Phenothiazine-Type Antioxidants Reveals Competing Objectives for Pharmaceutical Neuroprotection.Pharm Res. 2017 Feb;34(2):378-393. doi: 10.1007/s11095-016-2068-0. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 27896592
References
-
- Bertoni-Freddari C, Fattoretti P, Caselli U, Paoloni R, Meier-Ruge W. Vitamin E deficiency as a model of precocious brain aging: assessment by X-ray microanalysis and morphometry. Scanning Microsc. 1995;9:289–301. discussion 301-282. - PubMed
-
- Bertoni-Freddari C, Giuli C, Pieri C. Effect of chronic vitamin E deficiency on the synapses of cerebellar glomeruli in young rats. Mech Ageing Dev. 1984;24:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Bjorneboe A, Bjorneboe GE, Bodd E, Hagen BF, Kveseth N, Drevon CA. Transport and distribution of alpha-tocopherol in lymph, serum and liver cells in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;889:310–315. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter S. A Histochemical Study of Oxidative Enzymes in the Nervous System of Vitamin E-Deficient Rats. Neurology. 1965;15:328–332. - PubMed
-
- Castagna A, Le Grazie C, Accordini A, Giulidori P, Cavalli G, Bottiglieri T, Lazzarin A. Cerebrospinal fluid S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) and glutathione concentrations in HIV infection: effect of parenteral treatment with SAMe. Neurology. 1995;45:1678–1683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

