Integration of Golgi trafficking and growth factor signaling by the lipid phosphatase SAC1
- PMID: 18299350
- PMCID: PMC2265582
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200708109
Integration of Golgi trafficking and growth factor signaling by the lipid phosphatase SAC1
Abstract
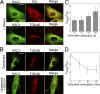
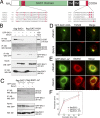
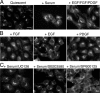
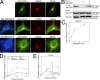
When a growing cell expands, lipids and proteins must be delivered to its periphery. Although this phenomenon has been observed for decades, it remains unknown how the secretory pathway responds to growth signaling. We demonstrate that control of Golgi phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI(4)P) is required for growth-dependent secretion. The phosphoinositide phosphatase SAC1 accumulates at the Golgi in quiescent cells and down-regulates anterograde trafficking by depleting Golgi PI(4)P. Golgi localization requires oligomerization of SAC1 and recruitment of the coat protein (COP) II complex. When quiescent cells are stimulated by mitogens, SAC1 rapidly shuttles back to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), thus releasing the brake on Golgi secretion. The p38 mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) pathway induces dissociation of SAC1 oligomers after mitogen stimulation, which triggers COP-I-mediated retrieval of SAC1 to the ER. Inhibition of p38 MAPK abolishes growth factor-induced Golgi-to-ER shuttling of SAC1 and slows secretion. These results suggest direct roles for p38 MAPK and SAC1 in transmitting growth signals to the secretory machinery.
Figures


References
-
- Acharya, U., A. Mallabiabarrena, J.K. Acharya, and V. Malhotra. 1998. Signaling via mitogen-activated protein-kinase kinase (MEK 1) is required for Golgi fragmentation during mitosis. Cell. 92:183–192. - PubMed
-
- Blagosklonny, M.V. 2006. Target for cancer therapy: proliferating cells or stem cells. Leukemia. 20:385–391. - PubMed
-
- Cavalli, V., F. Vilbois, M. Corti, M.J. Marcote, K. Tamura, M. Karin, S. Arkinstall, and J. Gruenberg. 2001. The stress-induced MAP kinase p38 regulates endocytic trafficking via the GDI:Rab5 complex. Mol. Cell. 7:421–432. - PubMed
-
- De Matteis, M.A., A. Di Campli, and A. Godi. 2005. The role of the phosphoinositides at the Golgi complex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1744:396–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

