Tetrathiomolybdate protects against bile duct ligation-induced cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis
- PMID: 18299419
- PMCID: PMC4222180
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.107.131227
Tetrathiomolybdate protects against bile duct ligation-induced cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis
Erratum in
- J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Jun;325(3):1062
Abstract
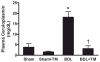
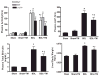
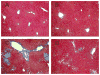
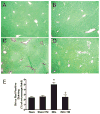
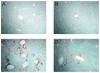
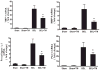
Tetrathiomolybdate (TM), a potent copper-chelating drug, was initially developed for the treatment of Wilson's disease. Our working hypothesis is that the fibrotic pathway is copper-dependent. Because biliary excretion is the major pathway for copper elimination, a bile duct ligation (BDL) mouse model was used to test the potential protective effects of TM. TM was given in a daily dose of 0.9 mg/mouse by means of intragastric gavage 5 days before BDL. All the animals were killed 5 days after surgery. Plasma liver enzymes and total bilirubin were markedly decreased in TM-treated BDL mice. TM also inhibited the increase in plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 seen in BDL mice. Cholestatic liver injury was markedly attenuated by TM treatment as shown by histology. Hepatic collagen deposition was significantly decreased, and it was paralleled by a significant suppression of hepatic smooth muscle alpha-actin and fibrogenic gene expression in TM-treated BDL mice. Although the endogenous antioxidant ability was enhanced, oxidative stress as shown by malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxyalkenals, hepatic glutathione/oxidized glutathione ratio, was not attenuated by TM treatment, suggesting the protective mechanism of TM may be independent of oxidative stress. In summary, TM attenuated BDL-induced cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis in mice, in part by inhibiting TNF-alpha and TGF-beta1 secretion. The protective mechanism seems to be independent of oxidative stress. Our data provide further evidence that TM might be a potential therapy for hepatic fibrosis.
Figures
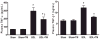

References
-
- Askari FK, Dick R, Mao M, Brewer GJ. Tetrathiomolybdate therapy protects against concanavalin A and carbon tetrachloride hepatic damage in mice. Exp Biol Med. 2004;229:857– 863. - PubMed
-
- Barón V, Muriel P. Role of glutathione, lipid peroxidation and antioxidants on acute bile-duct obstruction in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1472:173–180. - PubMed
-
- Bergheim I, Guo L, Davis MA, Duveau I, Arteel GE. Critical role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:592– 600. - PubMed
-
- Brewer GJ, Dick RD, Grover DK, LeClaire V, Tseng M, Wicha M, Pienta K, Redman BG, Jahan T, Sondak VK, et al. Treatment of metastatic cancer with tetrathiomolybdate, an anticopper, antiangiogenic agent: phase I study. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Brewer GJ, Dick R, Ullenbruch MR, Jin H, Phan SH. Inhibition of key cytokines by tetrathiomolybdate in the bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis. J Inorg Biochem. 2004;98:2160–2167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

