Lansoprazole Novel Effector Sites Revealed by Autoradiography: Relation to Helicobacter pylori, Colon, Esophagus and Others
- PMID: 18299709
- PMCID: PMC2243239
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.2007021
Lansoprazole Novel Effector Sites Revealed by Autoradiography: Relation to Helicobacter pylori, Colon, Esophagus and Others
Abstract
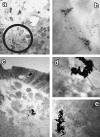
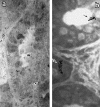
Lansoprazole uptake sites by two kinds of autoradiographic procedures were compared with recent literature. The uptake sites have been seen in the Helicobacter pylori, colonic epithelial cells, inflammatory cells, peripheral autonomic nerves and enterochromaffinlike cells as well as gastric parietal cells. Each uptake sites corresponded to the reported localization of P-type ATPase or acidic compartment.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; autoradiography; colon; inflammatory cell; lansoprazole.
Figures

References
-
- McCarty R.E. A plant biochemist’s view of H+-ATPases and ATP synthases. J. Exp. Biol. 1992;172:431–441. - PubMed
-
- Maeda M. Genes for gastric proton pump and their transcriptional regulation. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1996;116:91–105. - PubMed
-
- van Driel I.R., Callaghan J.M. Proton and potassium transport by H+/K(+)-ATPases. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1995;22:952–960. - PubMed
-
- Sachs G. Proton pump inhibitors and acid-related diseases. Pharmacotherapy. 1997;17:22–37. - PubMed

