Visual acuity and multifocal electroretinographic changes after arteriovenous crossing sheathotomy for macular edema associated with branch retinal vein occlusion
- PMID: 18301026
- PMCID: PMC2674764
- DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e31813c69df
Visual acuity and multifocal electroretinographic changes after arteriovenous crossing sheathotomy for macular edema associated with branch retinal vein occlusion
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the influence of arteriovenous (AV) sheathotomy on retinal function with central multifocal electroretinography (mfERG) in eyes with macular edema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO).
Methods: Fifteen patients (15 eyes) who underwent AV sheathotomy for macular edema secondary to BRVO were included in the study. Best-corrected visual acuity and mfERG responses from the most central seven hexagons were analyzed before and 6 months after the operation.
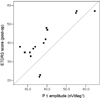
Results: The mean preoperative Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) score +/- SD was 34.1 +/- 12.7 letters (Snellen equivalent, 20/50) and significantly improved up to 40.5 +/- 10.9 letters (Snellen equivalent, 20/40) at 6 months after AV sheathotomy (P = 0.027, Wilcoxon signed rank test). The mean preoperative P1 amplitude +/- SD of the most central 7 hexagons was 39.30 +/- 10.86 nV/deg(2) for the affected eye versus 47.72 +/- 6.67 nV/deg(2) for the normal fellow (control) eye (P = 0.013, Mann-Whitney U test) and significantly increased up to 50.71 +/- 15.58 nV/deg at 6 months after the operation (P = 0.014, Wilcoxon signed rank test). Significant correlations between preoperative and postoperative ETDRS score and preoperative P1 amplitude were present (r = 0.929, P < 0.001; r = 0.768, P = 0.001; respectively [Spearman correlation]).
Conclusions: AV sheathotomy improved macular function and anatomical outcome as measured by ETDRS score and mfERG responses in patients with macular edema due to BRVO.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-term outcomes of vitrectomy with or without arteriovenous sheathotomy in branch retinal vein occlusion.Retina. 2007 Jan;27(1):49-54. doi: 10.1097/01.iae.0000221996.77421.69. Retina. 2007. PMID: 17218915 Clinical Trial.
-
Vitrectomy with or without arteriovenous adventitial sheathotomy for macular edema associated with branch retinal vein occlusion.Am J Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;138(6):907-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2004.06.061. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004. PMID: 15629280
-
Arteriovenous crossing sheathotomy versus intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection for treatment of macular edema associated with branch retinal vein occlusion.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008 Jul;246(7):967-74. doi: 10.1007/s00417-008-0830-7. Epub 2008 Apr 19. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18425522 Clinical Trial.
-
Surgical decompression of branch retinal vein occlusion via arteriovenous crossing sheathotomy: a prospective review of 15 cases.Retina. 1999;19(1):1-5. doi: 10.1097/00006982-199901000-00001. Retina. 1999. PMID: 10048366 Review.
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for macular oedema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 7;7(7):CD009510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32633861 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative evaluation between ranibizumab combined with laser and bevacizumab combined with laser versus laser alone for macular oedema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion.Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2014 Oct-Dec;21(4):296-301. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.142264. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25371633 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Dexamethasone Implant on Multifocal Electroretinography in Central Retinal Vein Occlusion.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2018 Jan-Mar;13(1):23-28. doi: 10.4103/jovr.jovr_118_16. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2018. PMID: 29403585 Free PMC article.
-
The Success of Cataract Surgery and the Preoperative Measurement of Retinal Function by Electrophysiological Techniques.J Ophthalmol. 2015;2015:401281. doi: 10.1155/2015/401281. Epub 2015 Oct 21. J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26576292 Free PMC article.
-
Electroretinography during embolization of an ophthalmic arteriovenous fistula.Surg Neurol Int. 2013 Mar 28;4:40. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.109653. Print 2013. Surg Neurol Int. 2013. PMID: 23607062 Free PMC article.
-
Fixation stability and implication for multifocal electroretinography in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration after anti-VEGF treatment.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct;254(10):1897-1908. doi: 10.1007/s00417-016-3323-0. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27080862
References
-
- Mitchell P, Smith W, Chang A. Prevalence and associations of retinal vein occlusion in Australia: The Blue Mountains Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996;114:1243–1247. - PubMed
-
- Branch Vein Occlusion Study Group. Argon laser photocoagulation for macular edema in branch vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984;98:271–282. - PubMed
-
- Greer DV, Constable IJ, Cooper RL. Macular oedema and retinal branch vein occlusion. Aust J Ophthalmol. 1980;8:207–209. - PubMed
-
- Osterloh MD, Charles S. Surgical decompression of branch retinal vein occlusion. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988;106:1469–1471. - PubMed
-
- Opremcak EM, Bruce RA. Surgical decompression of branch retinal vein occlusion via arteriovenous crossing sheathotomy: a prospective review of 15 cases. Retina. 1999;19:1–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

