Chronic fluoxetine treatment induces brain region-specific upregulation of genes associated with BDNF-induced long-term potentiation
- PMID: 18301726
- PMCID: PMC2248427
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/26496
Chronic fluoxetine treatment induces brain region-specific upregulation of genes associated with BDNF-induced long-term potentiation
Abstract
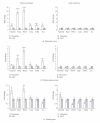
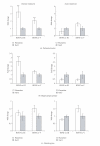
Several lines of evidence implicate BDNF in the pathogenesis of stress-induced depression and the delayed efficacy of antidepressant drugs. Antidepressant-induced upregulation of BDNF signaling is thought to promote adaptive neuronal plasticity through effects on gene expression, but the effector genes downstream of BDNF has not been identified. Local infusion of BDNF into the dentate gyrus induces a long-term potentiation (BDNF-LTP) of synaptic transmission that requires upregulation of the immediate early gene Arc. Recently, we identified five genes (neuritin, Narp, TIEG1, Carp, and Arl4d) that are coupregulated with Arc during BDNF-LTP. Here, we examined the expression of these genes in the dentate gyrus, hippocampus proper, and prefrontal cortex after antidepressant treatment. We show that chronic, but not acute, fluoxetine administration leads to upregulation of these BDNF-LTP-associated genes in a brain region-specific pattern. These findings link chronic effects of antidepressant treatment to molecular mechanisms underlying BDNF-induced synaptic plasticity.
Figures
References
-
- Bliss T, Collingridge G, Morris R. Synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. In: Andersen P, Morris R, Amaral D, Bliss T, O'Keefe J, editors. The Hippocampus Book. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press; 2007. pp. 343–474.
-
- Blum R, Konnerth A. Neurotrophin-mediated rapid signaling in the central nervous system: mechanisms and functions. Physiology. 2005;20(1):70–78. - PubMed
-
- Bramham CR, Messaoudi E. BDNF function in adult synaptic plasticity: the synaptic consolidation hypothesis. Progress in Neurobiology. 2005;76(2):99–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

