The Reelin receptors Apoer2 and Vldlr coordinate the patterning of Purkinje cell topography in the developing mouse cerebellum
- PMID: 18301736
- PMCID: PMC2242849
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001653
The Reelin receptors Apoer2 and Vldlr coordinate the patterning of Purkinje cell topography in the developing mouse cerebellum
Abstract
The adult cerebellar cortex is comprised of reproducible arrays of transverse zones and parasagittal stripes of Purkinje cells. Adult stripes are created through the perinatal rostrocaudal dispersion of embryonic Purkinje cell clusters, triggered by signaling through the Reelin pathway. Reelin is secreted by neurons in the external granular layer and deep cerebellar nuclei and binds to two high affinity extracellular receptors on Purkinje cells-the Very low density lipoprotein receptor (Vldlr) and apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (Apoer2). In mice null for either Reelin or double null for Vldlr and Apoer2, Purkinje cell clusters fail to disperse. Here we report that animals null for either Vldlr or Apoer2 individually, exhibit specific and parasagittally-restricted Purkinje cell ectopias. For example, in mice lacking Apoer2 function immunostaining reveals ectopic Purkinje cells that are largely restricted to the zebrin II-immunonegative population of the anterior vermis. In contrast, mice null for Vldlr have a much larger population of ectopic Purkinje cells that includes members from both the zebrin II-immunonegative and -immunopositive phenotypes. HSP25 immunoreactivity reveals that in Vldlr null animals a large portion of zebrin II-immunopositive ectopic cells are probably destined to become stripes in the central zone (lobules VI-VII). A small population of ectopic zebrin II-immunonegative Purkinje cells is also observed in animals heterozygous for both receptors (Apoer2(+/-): Vldlr(+/-)), but no ectopia is present in mice heterozygous for either receptor alone. These results indicate that Apoer2 and Vldlr coordinate the dispersal of distinct, but overlapping subsets of Purkinje cells in the developing cerebellum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

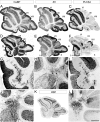

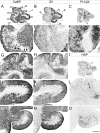
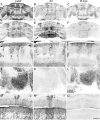
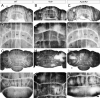

Similar articles
-
Binding of purified Reelin to ApoER2 and VLDLR mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of Disabled-1.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003 Apr 10;112(1-2):33-45. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(03)00032-9. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12670700
-
The Reelin receptors ApoER2 and VLDLR are direct target genes of HIC1 (Hypermethylated In Cancer 1).Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Oct 25;440(3):424-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.09.091. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 24076391
-
Reelin receptors in developing laminated brain structures of mouse and human.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Nov;20(10):2827-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03733.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15548227
-
From clusters to stripes: the developmental origins of adult cerebellar compartmentation.Cerebellum. 2006;5(2):77-88. doi: 10.1080/14734220600804668. Cerebellum. 2006. PMID: 16818382 Review.
-
[Corticohistogenesis and Reelin signal cascade].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000 Oct;20(4):169-74. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 11215402 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol: its regulation and role in central nervous system disorders.Cholesterol. 2012;2012:292598. doi: 10.1155/2012/292598. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Cholesterol. 2012. PMID: 23119149 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in the Hypoplastic Reeler Cerebellum.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 May 25;10:141. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00141. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27252624 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of topographic circuit zones in the cerebellum of scrambler mutant mice.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 Jul 22;7:122. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00122. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23885237 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome programs involved in the development and structure of the cerebellum.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Oct;78(19-20):6431-6451. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03911-w. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34406416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Phospholipase D2 Knock Out Mouse Has Ectopic Purkinje Cells and Suffers from Early Adult-Onset Anosmia.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 22;11(9):e0162814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162814. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27658289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hawkes R, Gravel C. The modular cerebellum. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36:309–327. - PubMed
-
- Hawkes R. An anatomical model of cerebellar modules. Prog Brain Res. 1997;114:39–52. - PubMed
-
- Herrup K, Kuemerle B. The compartmentalization of the cerebellum. Ann Rev Neurosci. 1997;20:61–90. - PubMed
-
- Oberdick J, Baader SL, Schilling K. From zebra stripes to postal zones: deciphering patterns of gene expression in the cerebellum. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Ozol K, Hayden J, Oberdick J, Hawkes R. Transverse zones in the vermis of the mouse cerebellum. J Comp Neurol. 1999;412:95–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

