Phase-I study of Innacell gammadelta, an autologous cell-therapy product highly enriched in gamma9delta2 T lymphocytes, in combination with IL-2, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 18301889
- PMCID: PMC11030608
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0491-8
Phase-I study of Innacell gammadelta, an autologous cell-therapy product highly enriched in gamma9delta2 T lymphocytes, in combination with IL-2, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: gamma9delta2 T lymphocytes have been shown to be directly cytotoxic against renal carcinoma cells. Lymphocytes T gammadelta can be selectively expanded in vivo with BrHPP (IPH1101, Phosphostim) and interleukin 2 (IL-2). A phase I Study was conducted in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) to determine the maximum-tolerated dose and safety of Innacell gammadelta, an autologous cell-therapy product based on gamma9delta2 T lymphocytes, in patients with mRCC.
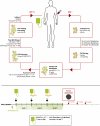
Experimental design: A 1-h intravenous infusion of gamma9delta2 T lymphocytes was administered alone during treatment cycle 1 and combined with a low dose of subcutaneous interleukin-2 (IL-2, 2 MIU/m2 from Day 1 to Day 7) in the two subsequent cycles (at 3-week intervals). The dose of gamma9delta2 T lymphocytes was escalated from 1 up to 8 x 10(9) cells.
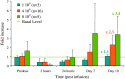
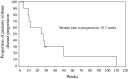
Results: Ten patients underwent a total of 27 treatment cycles. Immunomonitoring data demonstrate that gamma9delta2 T lymphocytes are initially cleared from the blood to reappear at the end of IL-2 administration. Dose-limiting toxicity occurred in one patient at the dose of 8 x 10(9) cells (disseminated intravascular coagulation). Other treatment-related adverse events (AEs) included mainly gastrointestinal disorders and flu-like symptoms (fatigue, pyrexia, rigors). Hypotension and tachycardia also occurred, especially with co-administered IL-2. Six patients showed stabilized disease. Time to progression was 25.7 weeks.
Conclusion: The data collected in ten patients with mRCC indicate that repeated infusions of Innacell gammadelta at different dose levels (up to 8 x 10(9) total cells), either alone or with IL-2 is well tolerated. These results are in favor of the therapeutic value of cell therapy with Innacell gammadelta for the treatment of cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Consultancy Agreement: Jaafar Bennounax. Clinical Investigator: Emmanuelle Bompas, Eve Marie Neidhardt, Frédéric Rolland, Irène Philip, Sylvie Négrier. Innate Pharma personnel: Céline Galéa, Samuel Salot, Sylvie Lafaye-de Micheaux, Jérôme Tiollier.
Figures

References
-
- Bukowski RM. Cytokine therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Semin Urol Oncol. 2001;19:148–54. - PubMed
-
- Common Toxicity Criteria (CTC) (1999) Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program. Common Toxicity Criteria, version 2.0. DCTD, NCI, NIH, DHHS
-
- Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Freeman S, Schwartz B, Shan M, Simantov R, Bukowski Study Group RM; TARGET. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:125–134. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa060655. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

