The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): MRI methods
- PMID: 18302232
- PMCID: PMC2544629
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21049
The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): MRI methods
Abstract
The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) is a longitudinal multisite observational study of healthy elders, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and Alzheimer's disease. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), (18F)-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG PET), urine serum, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers, as well as clinical/psychometric assessments are acquired at multiple time points. All data will be cross-linked and made available to the general scientific community. The purpose of this report is to describe the MRI methods employed in ADNI. The ADNI MRI core established specifications that guided protocol development. A major effort was devoted to evaluating 3D T(1)-weighted sequences for morphometric analyses. Several options for this sequence were optimized for the relevant manufacturer platforms and then compared in a reduced-scale clinical trial. The protocol selected for the ADNI study includes: back-to-back 3D magnetization prepared rapid gradient echo (MP-RAGE) scans; B(1)-calibration scans when applicable; and an axial proton density-T(2) dual contrast (i.e., echo) fast spin echo/turbo spin echo (FSE/TSE) for pathology detection. ADNI MRI methods seek to maximize scientific utility while minimizing the burden placed on participants. The approach taken in ADNI to standardization across sites and platforms of the MRI protocol, postacquisition corrections, and phantom-based monitoring of all scanners could be used as a model for other multisite trials.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
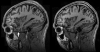
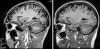
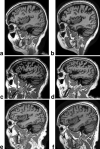


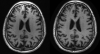
References
-
- Fox NC, Warrington EK, Freeborough PA, et al. Presymptomatic hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer's disease. A longitudinal MRI study. Brain. 1996;119:2001–2007. - PubMed
-
- Fox NC, Crum WR, Scahill RI, Stevens JM, Janssen JC, Rossor MN. Imaging of onset and progression of Alzheimer's disease with voxel-compression mapping of serial magnetic resonance images. Lancet. 2001;358:201–205. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Jack C, Jr, O'Brien PC, et al. Usefulness of MRI measures of entorhinal cortex vs hippocampus in AD. Neurology. 2000;54:1760–1767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

