Effects of protein oxidation on the structure and stability of model discoidal high-density lipoproteins
- PMID: 18302337
- PMCID: PMC2823073
- DOI: 10.1021/bi7023783
Effects of protein oxidation on the structure and stability of model discoidal high-density lipoproteins
Abstract
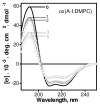
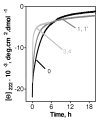
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) prevent atherosclerosis by removing cholesterol from macrophages and by providing antioxidants for low-density lipoproteins. Oxidation of HDLs affects their functions via the complex mechanisms that involve multiple protein and lipid modifications. To differentiate between the roles of oxidative modifications in HDL proteins and lipids, we analyzed the effects of selective protein oxidation by hypochlorite (HOCl) on the structure, stability, and remodeling of discoidal HDLs reconstituted from human apolipoproteins (A-I, A-II, or C-I) and phosphatidylcholines. Gel electrophoresis and electron microscopy revealed that, at ambient temperatures, protein oxidation in discoidal complexes promotes their remodeling into larger and smaller particles. Thermal denaturation monitored by far-UV circular dichroism and light scattering in melting and kinetic experiments shows that protein oxidation destabilizes discoidal lipoproteins and accelerates protein unfolding, dissociation, and lipoprotein fusion. This is likely due to the reduced affinity of the protein for lipid resulting from oxidation of Met and aromatic residues in the lipid-binding faces of amphipathic alpha-helices and to apolipoprotein cross-linking into dimers and trimers on the particle surface. We conclude that protein oxidation destabilizes HDL disk assembly and accelerates its remodeling and fusion. This result, which is not limited to model discoidal but also extends to plasma spherical HDL, helps explain the complex effects of oxidation on plasma lipoproteins.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Electrostatic effects on the stability of discoidal high-density lipoproteins.Biochemistry. 2005 Aug 2;44(30):10218-26. doi: 10.1021/bi050781m. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16042399
-
Mild oxidation promotes and advanced oxidation impairs remodeling of human high-density lipoprotein in vitro.J Mol Biol. 2008 Feb 29;376(4):997-1007. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.12.030. Epub 2007 Dec 23. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18190928 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic stabilization and fusion of apolipoprotein A-2:DMPC disks: comparison with apoA-1 and apoC-1.Biophys J. 2005 Apr;88(4):2907-18. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.055921. Epub 2005 Jan 28. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15681655 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative models for human apolipoprotein A-I bound to lipid in discoidal high-density lipoprotein particles.Biochemistry. 2002 Sep 10;41(36):10895-905. doi: 10.1021/bi020315m. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12206659 Review.
-
Structural studies of discoidal lipoprotein A-I.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001 Jun;58(7):885-93. doi: 10.1007/PL00000908. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001. PMID: 11497237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maturation of high-density lipoproteins.J R Soc Interface. 2009 Oct 6;6(39):863-71. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2009.0173. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J R Soc Interface. 2009. PMID: 19570799 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of oxidation on structural stability and remodeling of human very low density lipoprotein.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 9;49(44):9584-93. doi: 10.1021/bi101391z. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20919745 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-linking modifications of HDL apoproteins by oxidized phospholipids: structural characterization, in vivo detection, and functional implications.J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 14;295(7):1973-1984. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008445. Epub 2020 Jan 6. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31907281 Free PMC article.
-
HDL: bridging past and present with a look at the future.FASEB J. 2008 Dec;22(12):4044-54. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-117150. Epub 2008 Aug 20. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18716026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimized negative-staining electron microscopy for lipoprotein studies.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1830(1):2150-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.09.016. Epub 2012 Sep 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23032862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li L, Chen J, Mishra VK, Kurtz JA, Cao D, Klon AE, Harvey SC, Anantharamaiah GM, Segrest JP. Double belt structure of discoidal high density lipoproteins: Molecular basis for size heterogeneity. J Mol Biol. 2004;343(5):1293–1311. - PubMed
-
- Fielding CJ, Fielding PE. Molecular physiology of reverse cholesterol transport. J Lipid Res. 1995;36(2):211–228. - PubMed
-
- Asztalos BF. High density lipoprotein metabolism and progression of atherosclerosis: New insights from the HDL atherosclerosis treatment study. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2004;19(4):385–391. - PubMed
-
- Barter PJ, Nicholls S, Rye KA, Anantharamaiah GM, Navab M, Fogelman AM. Anti-inflammatory properties of HDL. Circ Res. 2004;95(8):764–772. - PubMed
-
- Parthasarathy S, Barnett J, Fong LG. High-density lipoprotein inhibits the oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1044:275–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

