Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor may modulate the post-transcription pathway of interleukin-6 expression in prostate carcinoma cells
- PMID: 18303206
- PMCID: PMC2526505
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.94
Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor may modulate the post-transcription pathway of interleukin-6 expression in prostate carcinoma cells
Abstract
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) can stimulate a variety of tumors including prostatic carcinoma. Research has recently shown that IL-6 may act to stimulate the progression of prostatic cancer. To date, little research has been performed to better understand the nature of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and the expression of IL-6. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of GM-CSF on the expression of IL-6 in prostate cancer-3 (PC-3) cells. The bone-derived PC-3 cell line was used in this study. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real- time PCR were performed to detect IL-6 mRNA expression. The IL-6 protein was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) after treatment with hGM-CSF. Our data indicated that IL-6 mRNA expression did not increase after treatment with hGM-CSF in comparison to the control group. However, the expression of IL-6 protein was increased compared to the control group. GM-CSF may modulate the post-transcription pathway of IL-6 expression in prostate carcinoma cells. Our data suggest that GM-CSF may have a role in IL-6-mediated development of prostate cancer.
Figures


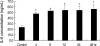
Similar articles
-
Expression and function of colony-stimulating factors and their receptors in human prostate carcinoma cell lines.Prostate. 1998 Feb 1;34(2):80-91. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0045(19980201)34:2<80::aid-pros2>3.0.co;2-n. Prostate. 1998. PMID: 9465939
-
Interleukin-6 production by human monocytes treated with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the presence of lipopolysaccharide of oral microorganisms.Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1998 Jun;13(3):173-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1998.tb00729.x. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1998. PMID: 10093532
-
Failure to detect interleukin (IL)-3 mRNA or protein in human keratinocytes: antibodies to granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor or IL-6 (but not IL-3) neutralize "IL-3" bioactivity.J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Mar;104(3):335-9. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12665370. J Invest Dermatol. 1995. PMID: 7860997
-
Interleukin-4 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mediates the upregulation of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 in RAW264.7 cells-a process in which p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling has an important role.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2016 Jun;49(3):344-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2014.06.008. Epub 2014 Aug 12. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2016. PMID: 25132397
-
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor expression is regulated at transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels in a murine bone marrow stromal cell line.Exp Hematol. 1994 Aug;22(9):924-32. Exp Hematol. 1994. PMID: 8062890
References
-
- National Statistical office. Republic of Korea. Korea Statistical Information System. [Dec., 31, 2002]. Available from: URL: http://kosis.nso.go.kr.
-
- Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:1–78. - PubMed
-
- Tan D, Wu X, Hou M, Lee SO, Lou W, Wang J, Janarthan B, Nallapareddy S, Trump DL, Gao AC. Interleukin-6 polymorphism is associated with more aggressive prostate cancer. J Urol. 2005;174:753–756. - PubMed
-
- Chung TD, Yu JJ, Spiotto MT, Bartkowski M, Simons JW. Characterization of the role of IL-6 in the progression of prostate cancer. Prostate. 1999;38:199–207. - PubMed
-
- Offner FA, Obrist P, Stadlmann S, Feichtinger H, Klingler P, Herold M, Zwierzina H, Hittmair A, Mikuz G, Abendstein B, Zeimet A, Marth C. IL-6 secretion by human peritoneal mesothelial and ovarian cancer cells. Cytokine. 1995;7:542–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

