Peak in matrix metaloproteinases-2 levels observed during recovery from olfactory nerve injury
- PMID: 18303576
- PMCID: PMC2428070
- DOI: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e3282f50c7b
Peak in matrix metaloproteinases-2 levels observed during recovery from olfactory nerve injury
Abstract
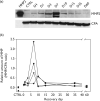
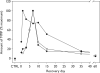
Matrix metalloproteineases are associated with extracellular remodeling that occurs in injury and repair processes in the central nervous system (CNS). We examined the role of MMP-2 in a model of olfactory nerve injury and found that MMP-2 levels increased several hours following injury, peaked at day 7 and then decreased rapidly. We previously reported a rapid increase in MMP-9, within 5 h after nerve injury, corresponding to neuronal degeneration and increased glial activity. In this study, we show that MMP-2 peaks later than MMP-9, at the onset of neuronal regeneration and repair. Using MMP-9 knockout mice, we determined that the MMP-2 increase is independent of MMP-9. Our data suggest that MMP-2 and MMP-9 may play different roles in the injury and repair processes.
Figures

References
-
- Romanic AM, White RF, Arleth AJ, Ohlstein EH, Barone FC. Matrix metalloproteinase expression increases after cerebral focal ischemia in rats: inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 reduces infarct size. Stroke. 1998;29:1020–1030. - PubMed
-
- Planas AM, Sole S, Justicia C. Expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in rat brain after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis. 2001;8:834–846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

