Death by a thousand cuts: granzyme pathways of programmed cell death
- PMID: 18304003
- PMCID: PMC2790083
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090404
Death by a thousand cuts: granzyme pathways of programmed cell death
Abstract
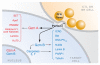
The granzymes are cell death-inducing enzymes, stored in the cytotoxic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, that are released during granule exocytosis when a specific virus-infected or transformed target cell is marked for elimination. Recent work suggests that this homologous family of serine esterases can activate at least three distinct pathways of cell death. This redundancy likely evolved to provide protection against pathogens and tumors with diverse strategies for evading cell death. This review discusses what is known about granzyme-mediated pathways of cell death as well as recent studies that implicate granzymes in immune regulation and extracellular proteolytic functions in inflammation.
Figures


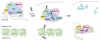
References
-
- Russell JH, Ley TJ. Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:323–70. - PubMed
-
- Gondek DC, Lu LF, Quezada SA, Sakaguchi S, Noelle RJ. Cutting edge: contact-mediated suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells involves a granzyme B-dependent, perforin-independent mechanism. J. Immunol. 2005;174:1783–86. - PubMed
-
- Grossman WJ, Verbsky JW, Tollefsen BL, Kemper C, Atkinson JP, Ley TJ. Differential expression of granzymes A and B in human cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets and T regulatory cells. Blood. 2004;104:2840–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

