Evolutionarily conserved amino acids that control TCR-MHC interaction
- PMID: 18304006
- PMCID: PMC3164820
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090421
Evolutionarily conserved amino acids that control TCR-MHC interaction
Abstract
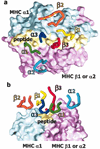
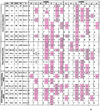
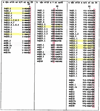
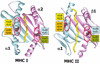
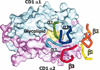
The rules for the conserved reaction of alphabeta T cell receptors (TCRs) with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins plus peptides are poorly understood, probably because thymocytes bearing TCRs with the strongest MHC reactivity are lost by negative selection. Thus, only TCRs with an attenuated ability to react with MHC appear on mature T cells. Also, the interaction sites between TCRs and MHC may be inherently flexible and hence difficult to spot. We reevaluated contacts between TCRs and MHC in the solved structures of their complexes with these points in mind. Relatively conserved amino acids in the TCR complementarity-determining regions (CDR) 1 and CDR2 are often used to bind exposed areas of the MHC alpha-helices. These areas are exposed because of small amino acids that allow somewhat flexible binding of the TCRs. The TCR amino acids involved are specific to families of variable (V) regions and to some extent different rules may govern the recognition of MHCI versus MHCII.
Figures






References
-
- Claman HN, Chaperon EA, Triplett RF. Thymus-marrow cell combinations. Synergism in antibody production. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966;122:1167–1171. - PubMed
-
- Mitchison NA. The carrier effect in the secondary response to hapten-protein conjugates. V. Use of antilymphocyte serum to deplete animals of helper cells. Eur J Immunol. 1971;1:68–75. - PubMed
-
- Rajewsky K. The carrier effect and cellular cooperation in the induction of antibodies. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971;176:385–392. - PubMed
-
- Gorer PA. Genetic and antigenic basis of tumor transplantation. J. Path. and Bact. 1937;44:691–697.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI-057485/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057485/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-17134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-19785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI017134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R56 AI017134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA-046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI-22295/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI022295/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

