Large-scale analysis of human heavy chain V(D)J recombination patterns
- PMID: 18304322
- PMCID: PMC2275228
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-7580-4-3
Large-scale analysis of human heavy chain V(D)J recombination patterns
Abstract
Background: The processes involved in the somatic assembly of antigen receptor genes are unique to the immune system and are driven largely by random events. Subtle biases, however, may exist and provide clues to the molecular mechanisms involved in their assembly and selection. Large-scale efforts to provide baseline data about the genetic characteristics of immunoglobulin (Ig) genes and the mechanisms involved in their assembly have recently become possible due to the rapid growth of genetic databases.
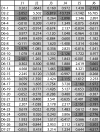
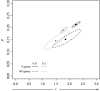
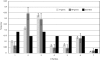
Results: We gathered and analyzed nearly 6,500 productive human Ig heavy chain genes and compared them with 325 non-productive Ig genes that were originally rearranged out of frame and therefore incapable of being biased by selection. We found evidence for differences in n-nucleotide tract length distributions which have interesting interpretations for the mechanisms involved in n-nucleotide polymerization. Additionally, we found striking statistical evidence for pairing preferences among D and J segments. We present a statistical model to support our hypothesis that these pairing biases are due to multiple sequential D-to-J rearrangements.
Conclusion: We present here the most precise estimates of gene segment usage frequencies currently available along with analyses regarding n-nucleotide distributions and D-J segment pair preferences. Additionally, we provide the first statistical evidence that sequential D-J recombinations occur at the human heavy chain locus during B-cell ontogeny with an approximate frequency of 20%.
Figures


References
-
- Matsuda F, Shin EK, Nagaoka H, Matsumara R, Haino M, Fukita Y, Taka-ishi S, Imai T, Riley JH, Anand R, Soeda E, Honjo T. Structure and physical map of 64 variable segments in the 3'0.8-megabase region of the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. Nat Genet. 1993;3:88–94. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-88. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
