The fine-scale and complex architecture of human copy-number variation
- PMID: 18304495
- PMCID: PMC2661628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.12.010
The fine-scale and complex architecture of human copy-number variation
Abstract
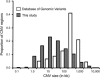
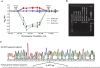
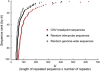
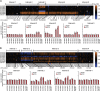
Despite considerable excitement over the potential functional significance of copy-number variants (CNVs), we still lack knowledge of the fine-scale architecture of the large majority of CNV regions in the human genome. In this study, we used a high-resolution array-based comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) platform that targeted known CNV regions of the human genome at approximately 1 kb resolution to interrogate the genomic DNAs of 30 individuals from four HapMap populations. Our results revealed that 1020 of 1153 CNV loci (88%) were actually smaller in size than what is recorded in the Database of Genomic Variants based on previously published studies. A reduction in size of more than 50% was observed for 876 CNV regions (76%). We conclude that the total genomic content of currently known common human CNVs is likely smaller than previously thought. In addition, approximately 8% of the CNV regions observed in multiple individuals exhibited genomic architectural complexity in the form of smaller CNVs within larger ones and CNVs with interindividual variation in breakpoints. Future association studies that aim to capture the potential influences of CNVs on disease phenotypes will need to consider how to best ascertain this previously uncharacterized complexity.
Figures

References
-
- Ottolenghi S., Lanyon W.G., Paul J., Williamson R., Weatherall D.J., Clegg J.B., Pritchard J., Pootrakul S., Boon W.H. The severe form of alpha thalassaemia is caused by a haemoglobin gene deletion. Nature. 1974;251:389–392. - PubMed
-
- Taylor J.M., Dozy A., Kan Y.W., Varmus H.E., Lie-Injo L.E., Ganesan J., Todd D. Genetic lesion in homozygous alpha thalassaemia (hydrops fetalis) Nature. 1974;251:392–393. - PubMed
-
- Ottolenghi S., Comi P., Giglioni B., Tolstoshev P., Lanyon W.G., Mitchell G.J., Williamson R., Russo G., Musumeci S., Schillro G. Delta-beta-thalassemia is due to a gene deletion. Cell. 1976;9:71–80. - PubMed
-
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D.S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: The genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986;232:193–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

